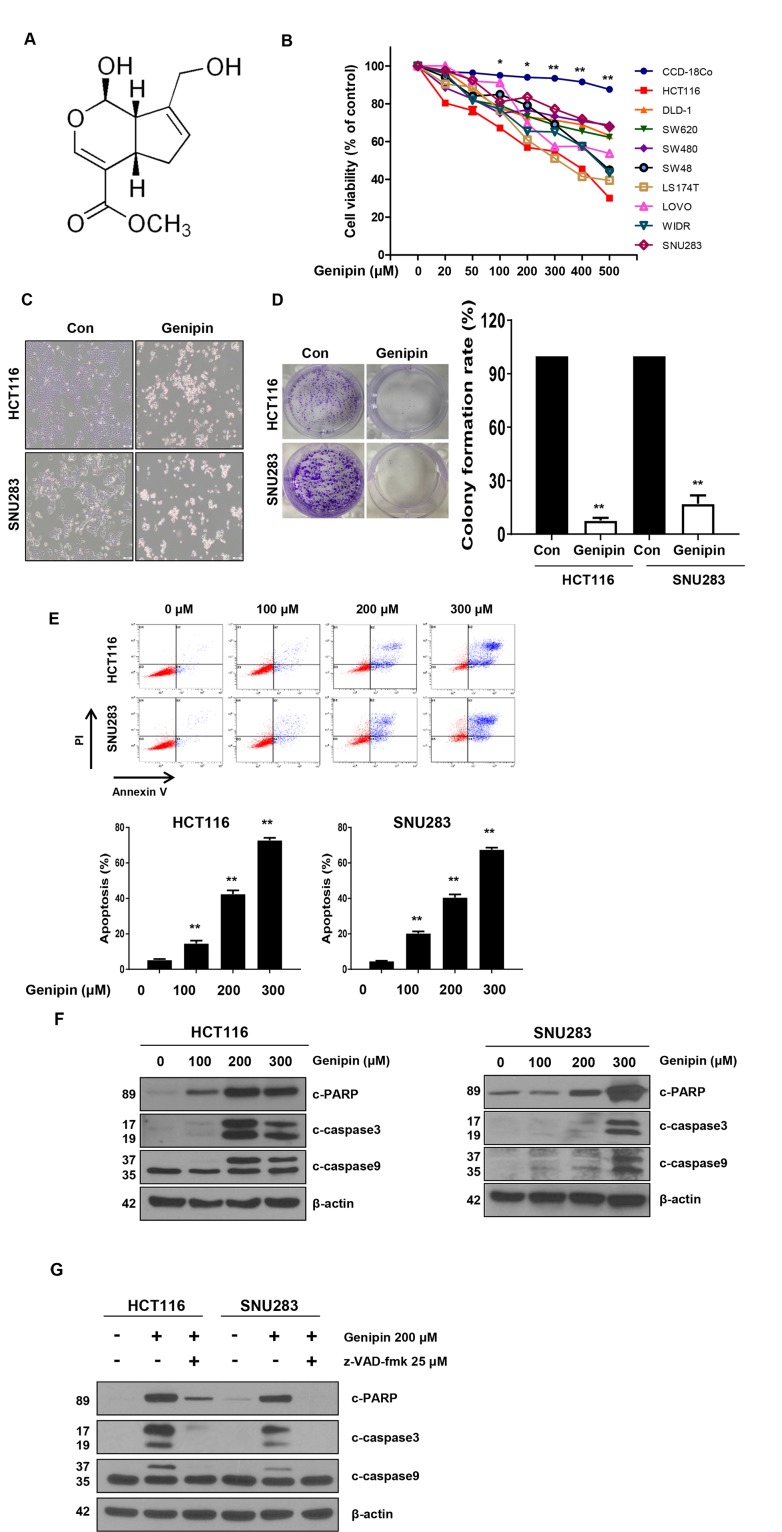
Figure 1.
(A) Chemical structure of genipin. (B) The cell viability of colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines measured by the MTT assay following treatment with 0–500 μM genipin for 24 h. (C) HCT116 and SNU283 cells were treated with 200 μM genipin, and cell morphology was examined by microscopy. (D) HCT116 and SNU283 cells were treated with 200 μM genipin. After 14 days, cells were stained with crystal violet and photographed (colonies shown on left). The graphs represent the percentage of stained colonies (right). (E) HCT116 and SNU283 cells treated with genipin were stained with annexin V and propidium iodide, and then were analyzed by FACS analysis. (F) The levels of cleaved PARP, CASP3, and CASP9 were detected by western blotting. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (G) Cells were pretreated with 25 μM z-VAD-fmk for 30 min and then treated with 200 μM genipin for 24 h. The levels of cleaved PARP, CASP3, and CASP9 were detected by western blotting. β-Actin was used as a loading control for each lane. Data are expressed as the means of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05.