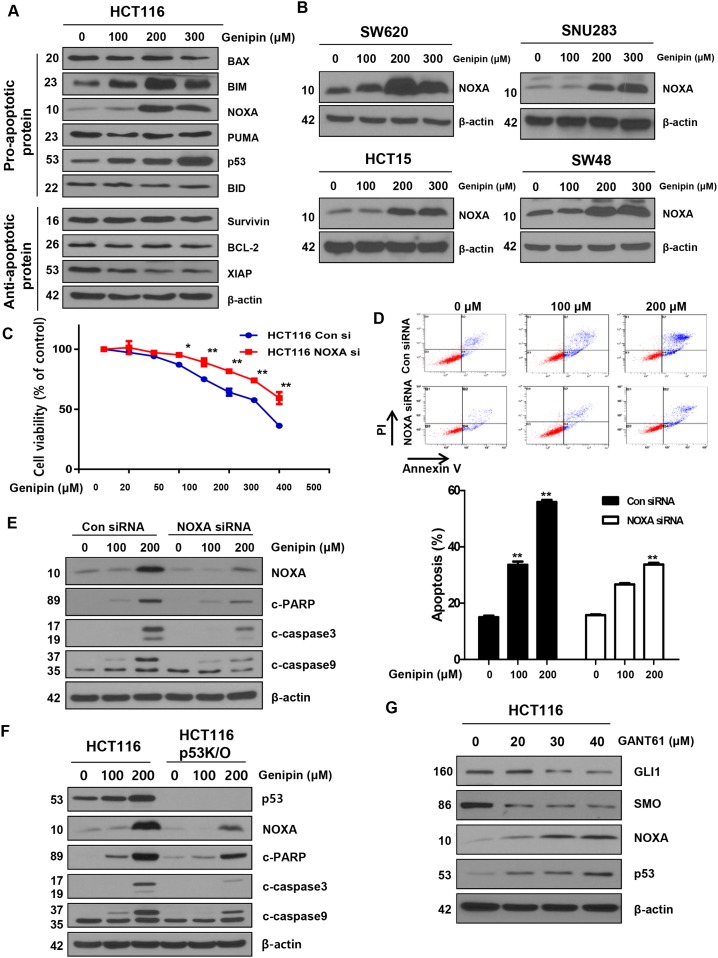
Figure 3.
(A) HCT116 cells were treated with genipin (100, 200, and 300 μM) for 24 h, and then the protein levels of BAX, BIM, NOXA, PUMA, p53, BID (pro-apoptotic protein), survivin, BCL2, and XIAP (anti-apoptotic protein) were determined by western blotting. (B) SW620, SNU283, HCT15, and SW48 cells were treated with genipin (0, 100, 200, and 300 μM) for 24 h, and then NOXA protein levels were analyzed by western blotting. (C) HCT116 cells were transfected with a control or NOXA siRNA. The MTT assay was used to evaluate the effects of NOXA expression on proliferation. (D) HCT116 cells transfected with control or NOXA siRNA were stained with annexin V and propidium iodide (PI), and then were evaluated by using FACS analysis. (E) The levels of cleaved PARP, CASP3, and CASP9 were detected by western blotting. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (F) The levels of cleaved PARP, CASP3, and CASP9 were examined using western blotting after treatment with genipin (0, 100, and 200 μM) for 24 h. (G) HCT116 cells were treated with GANT61 (0, 20, 30, and 40 μM) for 48 h, and then the expression levels of GLI1, SMO, NOXA, and p53 were detected by western blotting. Data are expressed as the means of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05.