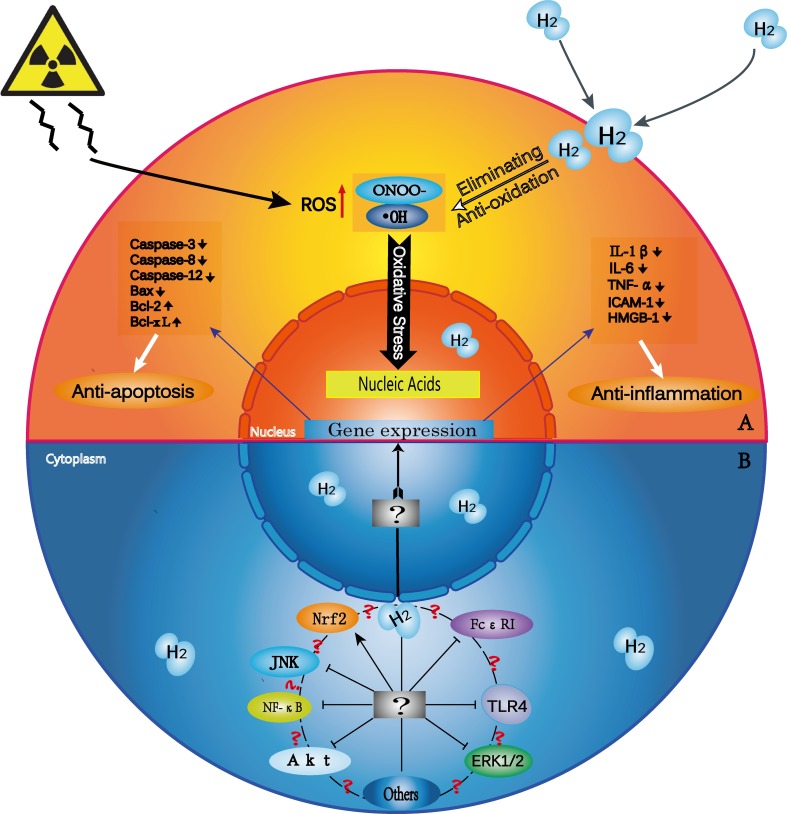
Figure 1. H2 biological effects and possible mechanisms of action.
(A) H2 has selective anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic properties. Exogenous damage due to such factors as radiation induces excess cellular ROS production. H2 penetrates biomembranes and effectively reaches cell nuclei. H2 selectively scavenges ·OH and ONOO- and thus prevents DNA damage. H2 also downregulates the expression of pro-inflammatory and inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, ICAM-1, and HMGB-1, and of pro-apoptotic factors, such as caspase-3, caspase-12, caspase-8 and Bax. H2 upregulates the expression of anti-apoptotic factors, such as Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL. (B) H2 modulates signal transduction within and between many pathways. ?¶The exact targets and molecular mechanisms of H2 are unknown. ?: Does cross-talk occur among various signaling pathways? If so, how is it triggered? Further studies should explore other signaling pathways that may take part in H2-related disease mitigation.