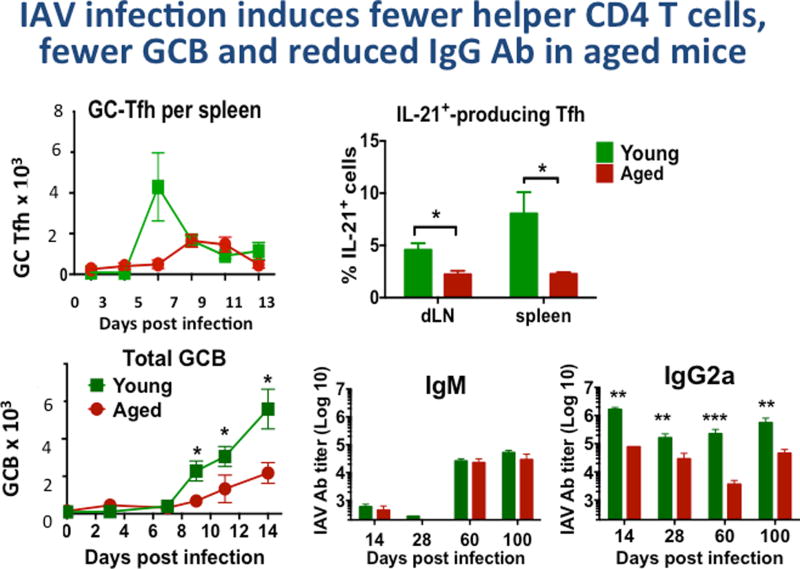
Figure 1. IAV infection of Aged Mice induces fewer helper CD4 T cells, fewer GCB cell and reduced IgG Ab.
Young (2–3 mo.) and aged (20 mo.) B6 female mice, were infected with A/PR8/34 influenza (EID 500, corresponding to 0.2LD50 for young B6 mice) introduced by the intranasal route as in previous studies [29]. We determined generation of helper T cell subsets and germinal center B cells (GCB). GC-Tfh (CXCR5hi, Bcl6hi, GL-7+ CD4+ T cells by FACS) were enumerated in groups of mice harvested at 0, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11 and 13 days post infection. Potential helper CD4 T cells producing IL-21 were determined by intracellular cytokine staining [7] and are expressed as the % of total CD4 T cells.
We determined total GCB by FACS staining of CD19+ cells with labeled Ab to CXCR5, Bcl6 and GL-7. In a similar more extended kinetics experiment, serum was collected from young and aged mice at, 28, 60, 100 dpi and IgM, IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b and IgG3 specific for PR8 were determined by isotype-specific ELISA as previously [16]. Significant differences between values for young and aged groups are indicated by * is ≤0.05, **≤0.01, ***≤0.005. TFH were also reduced in age, as were plasma cells in bone marrow and spleen at 40 and 100 days (not shown). Total IgG, IgG1 and IgG2b were also reduced significantly in the aged compared to young at each time point (not shown).