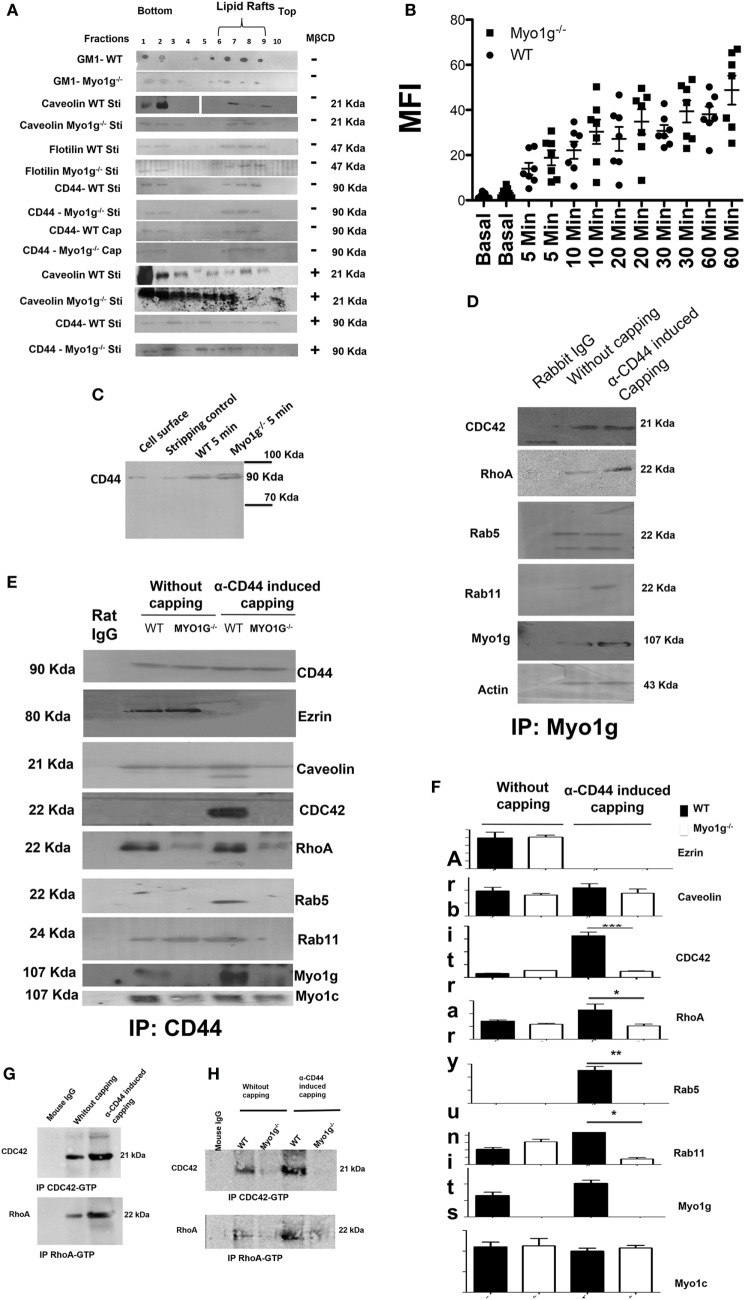
Figure 5.
The absence of Myo1g alters the recycling of CD44. (A) Western blot of CD44, caveolin, flotilin, GM1 in activated or cap-induced B cells from WT or Myo1g-deficient B cells, treated or not with MβCD (n = 3). (B) Resting B- lymphocytes were treated with FITC-hyaluronic acid (HA) for 1 h at 4°C and were then incubated at 37°C for different time points. After incubation, the fluorescence was quenched by the addition of 0.5% trypan blue for 30 s, and the cells were extensively washed with 1× phosphate-buffered saline. Finally, the cells were fixed and fluorescence was analyzed by flow cytometry. The graph shows the percentage of HA endocytosed by B-lymphocytes. The results are derived from the analysis of seven independent experiments and presented as mean ± SD. (C) Immunodetection of intracellular CD44 in WT or Myo1g−/− activated B cells induced to cap with the NIMR8 mAb (n = 3). (D) Immunoprecipitation of Myo1g in activated B lymphocytes from WT mice, comparing cells with or without CD44-induced capping (n = 3). (E) Immunoprecipitation of CD44 from activated B cells from WT or Myo1g-deficient mice, comparing cells with or without CD44 capping (n = 3). (F) Densitometry analysis of GTPases associated with the CD44-recycling complex. Images were analyzed using the ImageJ software to obtain the values. One-way ANOVA test was used in this graph, values are mean ± SD (n = 3) (*P < 0.05) (**P < 0.01). (G) Immunoprecipitation of CDC42-GTP and RhoA-GTP in activated or α-CD44-induced-capping B lymphocytes from WT mice (n = 3). (H) Immunoprecipitation of CDC42-GTP and RhoA-GTP from activated B cells from WT or Myo1g-deficient mice, comparing cells with or without CD44 capping (n = 3).