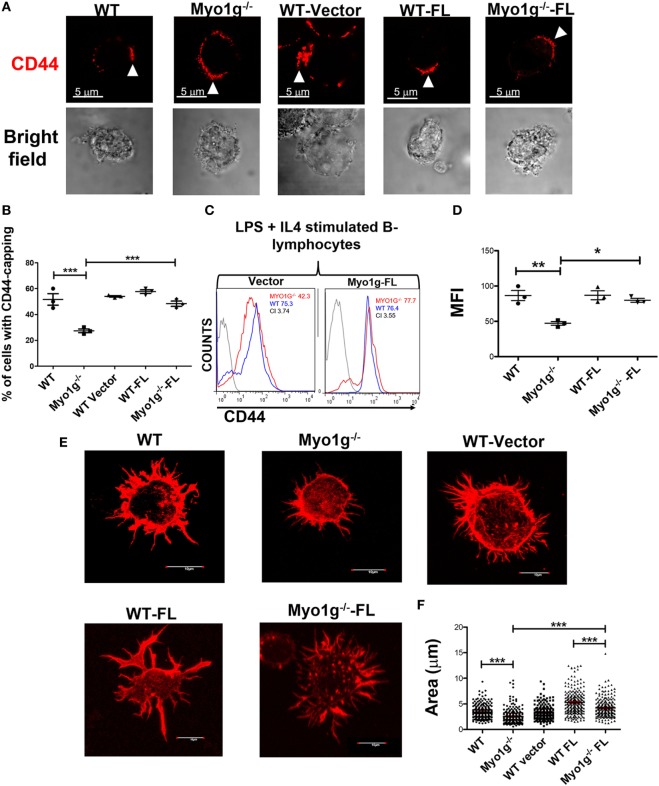
Figure 9.
Transfection with full-length Myo1g rescue CD44-dependent capping and spreading in Myo1g-deficient B-cells. (A) Confocal images of LPS plus IL4-activated B cells from WT, Myo1g−/−, WT, or Myo1g−/− transfected with an empty vector or Myo1g-FL. Arrows illustrate the localization of CD44 in B lymphocytes (scale bar 5 µm). (B) Percentage of cells with CD44-capping. Images of randomly selected files were taken and the percentage of B lymphocytes with capping was calculated. A total of 200 cells per data set from three independent experiment were analyzed. One-way ANOVA test was used in these experiments, values are mean ± SD (***P < 0.001) (n = 3). (C) Representative expression of CD44 in LPS plus IL4-activated B cells transfected or not with Myo1g-FL from WT or Myo1g-deficient B lymphocytes, the graph shows the expression of CD44 in B lymphocytes (10,000 events in a gate of B220 + B cells). (D) Expression of CD44 in LPS plus IL4-activated B cells transfected or not with Myo1g-FL from WT or Myo1g-deficient B lymphocytes. One-way ANOVA test was used in these experiments, values are mean ± SD (* P < 0.05, **P < 0.01) (n = 3). (E) Confocal images of activated B cells from WT or Myo1g-deficient mice over NIMR8. (F) The area of spread B lymphocytes was evaluated, a total of 150 cells per data set from three independent experiments were analyzed. One-way ANOVA test was used in these experiments, values are mean ± SD (***P < 0.001).