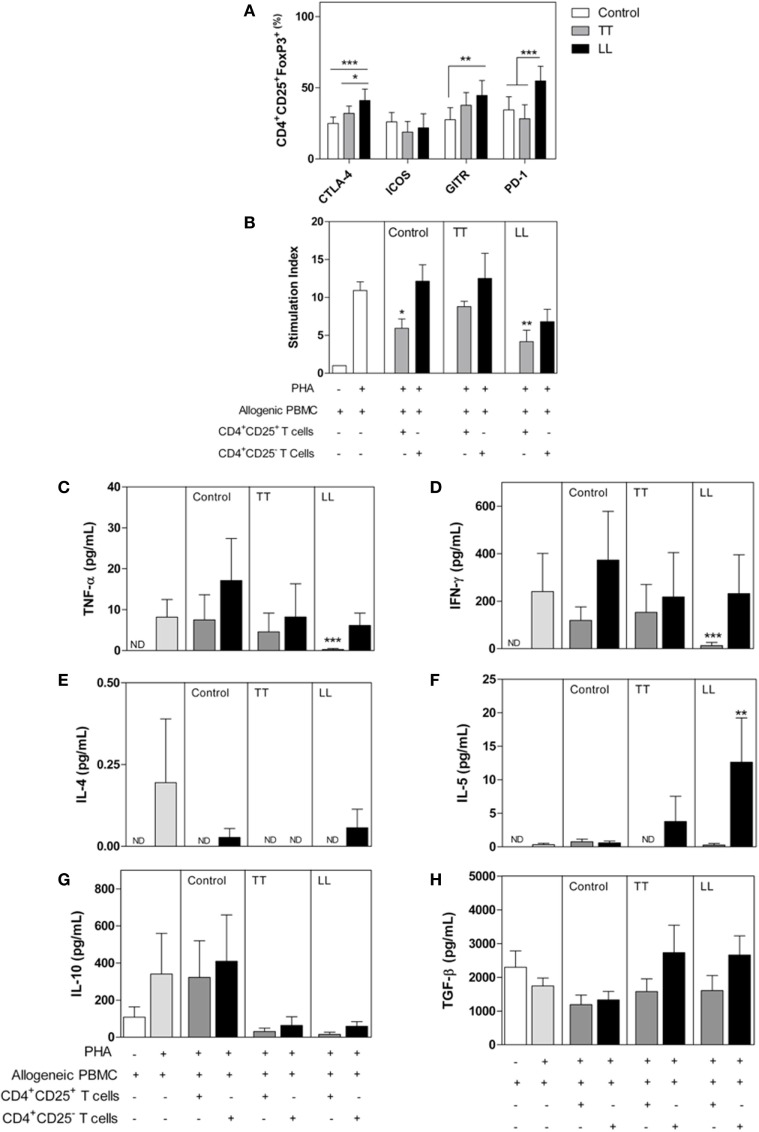
Figure 1.
Phenotype and functional characterization of CD4+CD25+ T cells in leprosy patients. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated from patients with tuberculoid (TT, n = 12) and lepromatous leprosy (LL, n = 12), as well as from healthy control subjects (n = 12). (A) The frequency of CD25+ and FoxP3+ cells and expression of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4), GITR, ICOS, and PD-1 were determined by flow cytometry. (B) Allogeneic PBMC (1 × 105 cells/well) was cultured with medium only, PHA, PHA plus CD4+CD25+ T, or CD4+CD25− T cells (1 × 104 cells/well) from patients or control subjects. Proliferation was determined after 4 days of culture by CFSE dilution analyzed by flow cytometry. The results are expressed as the means ± SEM of the stimulation index of proliferation. IFN-γ (C), TNF-α (D), IL-4 (E), IL-5 (F), IL-10 (G), and TGF-β (H) levels were determined in supernatants from cultures of suppression assays. The results are presented as the means ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001, compared with control subjects using ANOVA and the Bonferroni posttest. For the suppressive assay (B), the results are expressed as the means ± SEM; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001, compared with the proliferation of allogeneic PBMCs cultured with PHA. ND, not detected.