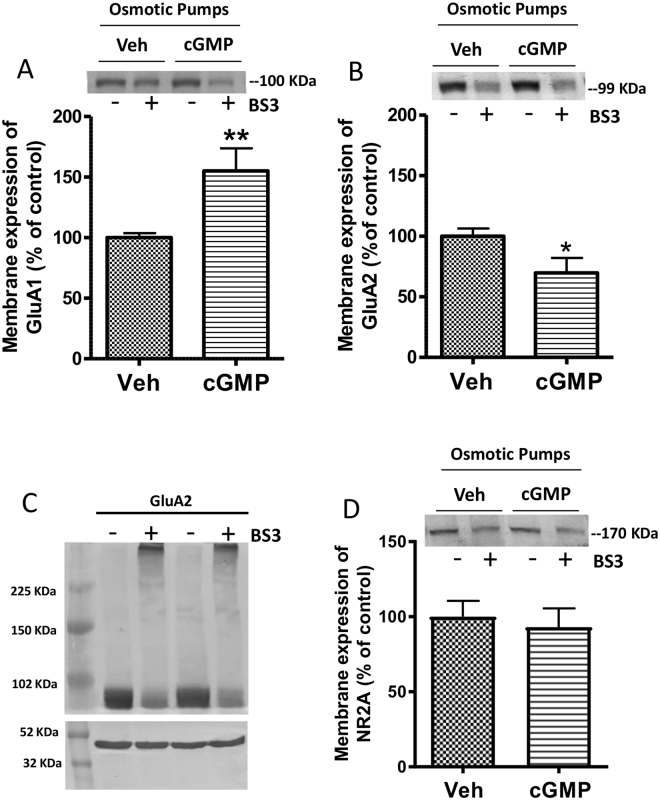
Figure 1.
Chronic intracerebral administration of extracellular cGMP increases membrane expression of the GluA1 (A) and decreases GluA2 (B) subunits of AMPA receptors in cerebellum in vivo. Membrane expression of NR2A in the same samples is not affected by extracellular cGMP (D). For one group of rats the osmotic pumps were filled with 240 µM cGMP in sterile saline (cGMP) and for the other group with the vehicle solution, sterile saline (veh). These pumps released 0.25 μL per hour during 28 days. Cerebellum of rats was dissected and membrane expression of each subunit was analyzed using the BS3 crosslinker procedure as described in Methods. (C) Monomeric and cross-linked bands of GluA2 and actin from western blot are shown. Values are expressed as percentage of control rats (vehicle) and are the mean ± SEM of 16–19 rats per group. The unpaired Student’s t-test was performed. Values significantly different are indicated by asterisks *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.