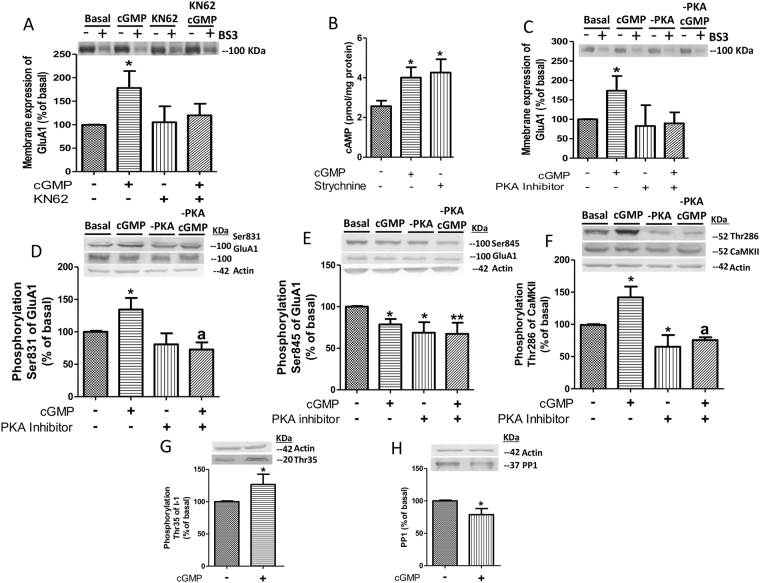
Figure 6.
Extracellular cGMP increases membrane expression of GluA1 subunit through activation of the cAMP-PKA-I1-PP1-CaMKII pathway. (A) Extracellular cGMP was added to cerebellar slices in the absence or the presence of an inhibitor of CaMKII (KN62, 10 µM) and membrane expression of GluA1 was analyzed. (B) cAMP levels in cerebellar slices after administration of 40 nM cGMP or 75 µM strychnine. (C–F) Extracellular cGMP was added to cerebellar slices in the absence or the presence of an inhibitor of PKA (1 µM 14–22 Amide) and membrane expression of GluA1 (C) and its phosphorylation at Ser831 (D), at Ser845 (E) and phosphorylation of CaMKKI at Thr286 (F) were analyzed. (G,H) Content of protein phosphatase inhibitor-1 (I1) phosphorylated at Thr 35 (G) and PP1 (H) after treatment with extracellular cGMP. Non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test (in A,C–F), one-way analysis of variance (in B) and the unpaired Student’s t-test (in G,H) were performed. Values are expressed as percentage of basal and are the mean ± SEM of 10–15 rats. Values significantly different from basal are indicated by asterisk *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Values significantly different from cGMP treatment are indicated by a p < 0.05.