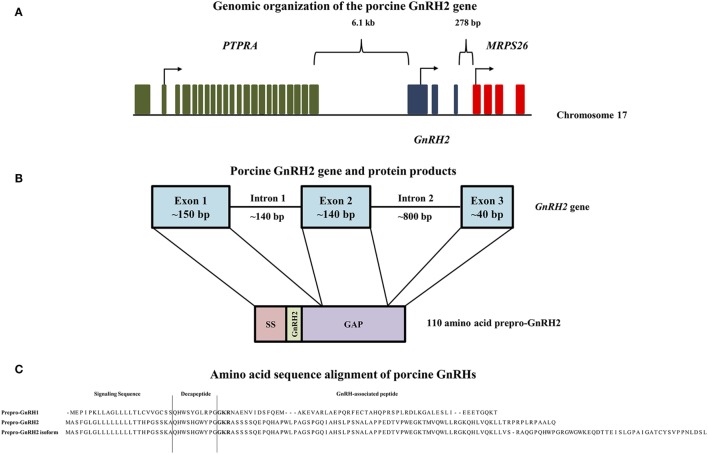
Figure 1.
Genomic organization of the porcine GnRH2 gene and its products. (A) The PTPRA gene (green) is located 6.1 kb upstream, whereas the MRPS26 gene (red) is positioned 278 bp downstream of the porcine GnRH2 gene (blue) on chromosome 17. Arrows indicate start codons for each gene. (B) The porcine GnRH2 gene contains three coding exons and two introns. Exon 1 (~150 bp) of the porcine GnRH2 gene encodes the signaling sequence (SS), mature GnRH2 decapeptide, and a portion of the GnRH-associated peptide (GAP). Exon 2 (~140 bp) and exon 3 (~40 bp) encode the remaining GAP sequence. Note that introns and exons are not drawn to scale. (C) Amino acid sequence alignments of predicted porcine prepro-GnRH2 isoforms (NCBI accession numbers XP_005672842 and XP_013840618) with porcine prepro-GnRH1 (NCBI accession number NP_999439). Prepro-GnRH1 is 91 amino acids in length compared with prepro-GnRH2, which has 110 residues. An isoform of prepro-GnRH2 (143 amino acids) is also predicted to be produced from the porcine GnRH2 gene due to alternative splicing. The amino acids that correspond to the SS, the mature decapeptide, and the GAP are indicated. The proteolytic cleavage sites are highlighted in bold.