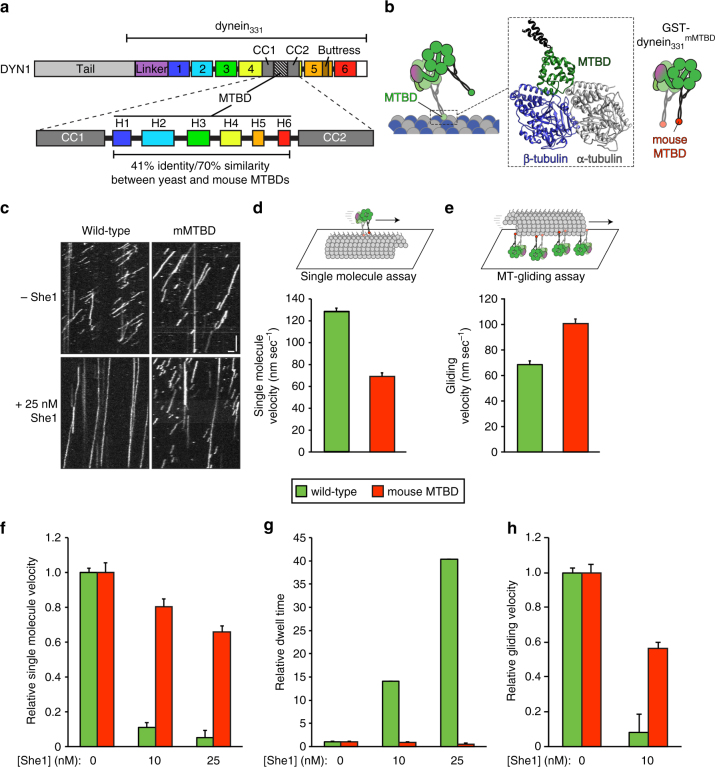
Fig. 6.
A dynein motor with a mutated MTBD exhibits reduced She1 sensitivity. a Schematic representation of the yeast dynein heavy chain (DYN1) with domain structure indicated (domains 1–6 represent the individual AAA domains; CC coiled coil; H1–H6, helices that comprise the MTBD). b Cartoon representation with homology model of the yeast dynein MTBD bound to alpha and beta-tubulin (green, MTBD; dark gray, CC1 and CC2; generated using one-to-one threading of yeast DYN1 sequence into 3J1T45 on the Phyre2 server71). c Kymographs depicting single-molecule motility of GST–dynein331 and GST–dynein331 mMTBD in the absence (top) or presence (bottom) of 25 nM She1 (horizontal scale bar, 2 µm; vertical scale bar, 1 min). d, e Plots depicting mean velocity of GST–dynein331 and GST–dynein331 mMTBD in single-molecule (d) and ensemble microtubule gliding assays (e; error bars, standard error). f, g Plots depicting effects of She1 on the relative velocity (f) and dwell time (g) of single molecules of GST–dynein331 and GST–dynein331 mMTBD. h Plot depicting effects of She1 on the relative microtubule gliding velocity of coverslip-immobilized GST–dynein331 and GST–dynein331 mMTBD (error bars, standard error; n ≥ 147 individual motors for each condition for single-molecule assay; n ≥ 21 microtubules for each condition for the ensemble motility assay); Supplementary Figs. 4 and 5)