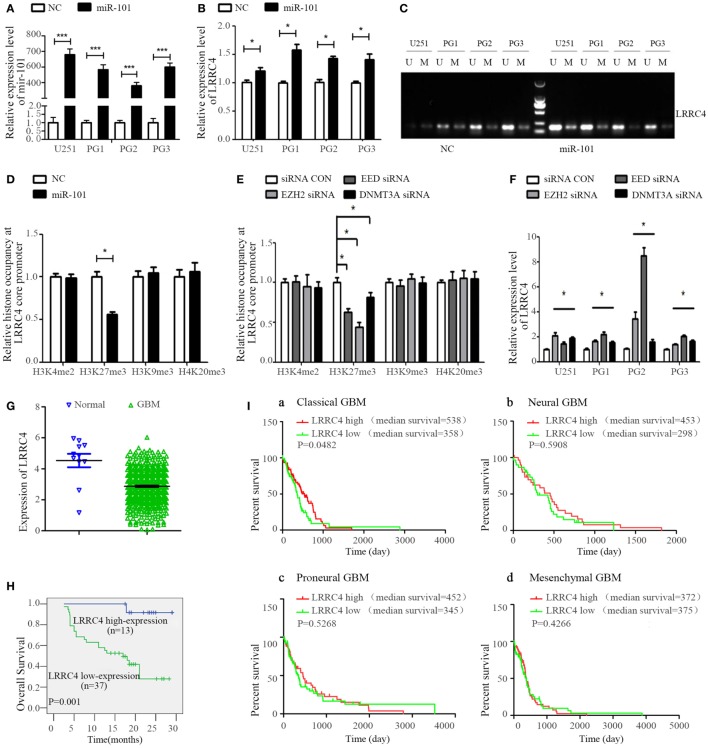
Figure 4.
miR-101 reversed the hypermethylation of LRRC4 and induced LRRC4 re-expression in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) cells by targeting EZH2, EED, and DNMT3A. (A) The miR-101 level was increased after GBM cells were transfected with miR-101/NC (*P < 0.001). (B) miR-101 promoted LRRC4 mRNA expression (*P < 0.05). (C) miR-101 reversed the hypermethylation status of LRRC4 by MSP in GBM cells; U, unmethylated primer; M, methylated primer. (D) H3K27me3 occupancy of the LRRC4 core promoter was inhibited by miR-101. A ChIP assay was used to detect the H3K4me2, H3K27me3, H3K9me3, and H4K20me3 occupancy of the LRRC4 core promoter (*P < 0.05). (E) H3K27me3 occupancy of the LRRC4 core promoter was inhibited by EZH2 siRNA, EED siRNA, and DNMT3A siRNA. A ChIP assay was performed to detect the H3K4me2, H3K27me3, H3K9me3, and H4K20me3 occupancy of the LRRC4 core promoter. GBM cells were transfected with EZH2 siRNA, EED siRNA, and DNMT3A siRNA (*P < 0.05). (F) LRRC4 expression was increased after GBM cells were transfected with EZH2 siRNA, EED siRNA, DNMT3A siRNA, or a siRNA NC (*P < 0.05). (G) LRRC4 expression in GBMs and normal brain tissues from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). (H) Kaplan–Meier curve analysis indicated that the high LRRC4 expression was correlated with a better survival prognosis in astrocytoma patients (n = 50). (I) Kaplan–Meier curve analysis in four subtypes of TCGA GBM patients (classical, neural, proneural, and mesenchymal) stratified by LRRC4 expression. Classical subtype GBM patients with high LRRC4 expression had a better overall survival, and the median OS was higher in high LRRC4 expression than in low LRRC4 expression patients with neural and proneural GBM.