Figure 1. Dual mechanism of action of avelumab.
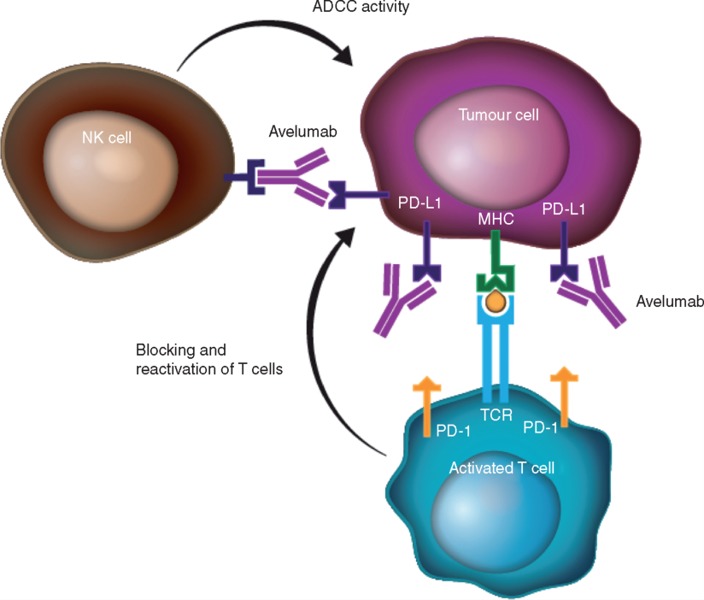
Avelumab, a fully human anti-PD-L1 IgG1 monoclonal antibody with an unmodified Fc region exerts anti-tumor immunity via: (1) blockade of the immune-inhibitory PD-1/PD-L1 interaction leading to reactivation of a T-cell mediated anti-tumor responses and (2) induction of natural killer cell-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) of tumor cells via interaction of CD16 (FcɣRIIIa) on NK cells with the Fc portion of the anti-PD-L1 mAb; Fc, fragment crystallizable; IgG1, immunoglobulin G1; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; NK, natural killer; PD-1, programmed death-1; PD-L1, programmed death ligand-1; TCR, T-cell receptor. Adapted with permission from Chin K, et al. Ann Oncol. 2017; 28: 1658-1666.
