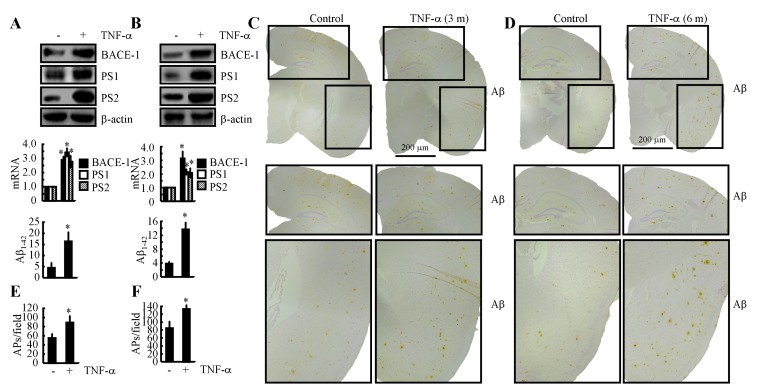
Figure 7. Intranasal administration of TNF-α accelerates Aβ deposition in APs by inducing the expression of BACE-1, PS1 and PS2 during the course of AD development.
A. TNF-α (10 ng/20 µl/d) was nasally administered to 3-month-old WT mice for 7 days (n = 10). The protein and mRNA expression of BACE-1, PS1 and PS2 were determined by western blot and qRT-PCR. The total amounts of β-actin and GAPDH served as internal controls. The production of Aβ1-42 was determined by western blot and Aβ1-42 enzyme immunoassay kits. B. n2a cells were treated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 24 h before total mRNA and protein was extracted. The protein and mRNA expression of BACE-1, PS1 and PS2 were determined by western blot and qRT-PCR. The total amounts of β-actin and GAPDH served as internal controls. The production of Aβ1-42 was determined by western blot and Aβ1-42 enzyme immunoassay kits. C.-F. 3-month-old APP/PS1 mice were nasally administered TNF-α (10 ng/20 µl/d) for 3 or 6 months before Aβ deposition in APs was determined (n = 6). C., D. Aβ immunoreactivity was determined using an immunohistochemistry assay. E., F. APs/field in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice were analysed by counting the number of APs in images of the immunohistochemically stained tissue. *, p < 0.05 with respect to the vehicle-treated control.