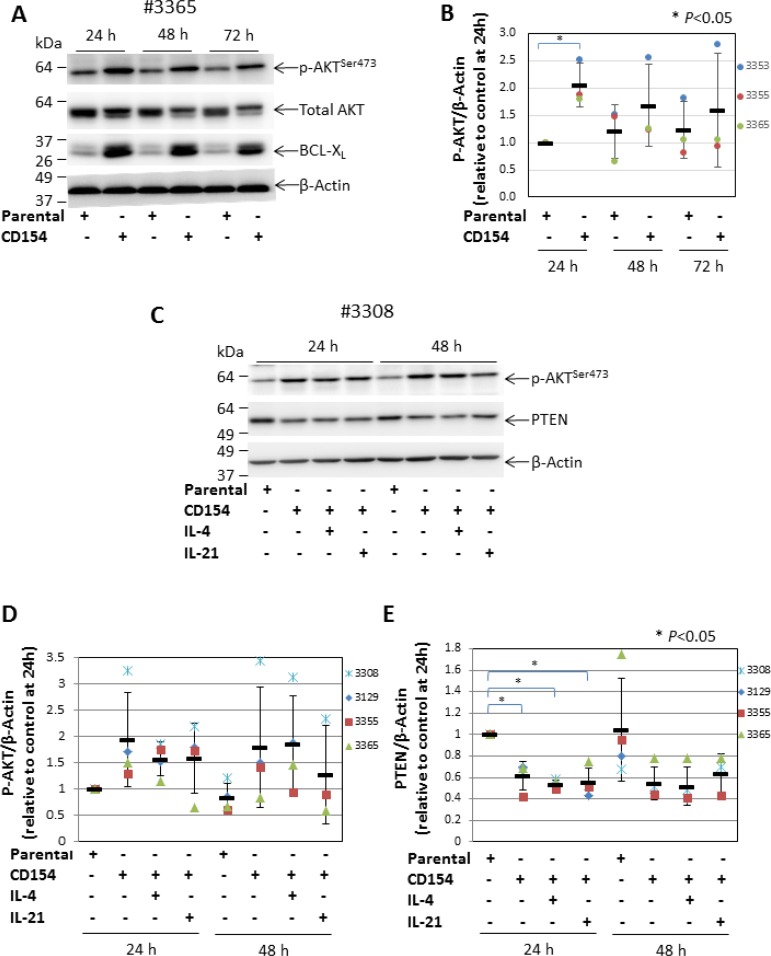
Figure 1. CD40 stimulation-induced AKT activation is associated with decreased expression of PTEN.
(A) CLL cells were cultured on a monolayer of parental control or CD154-expressing fibroblasts for 24, 48 and 72 h. At the indicated time points, CLL cells were harvested and analysed for the levels of p-AKT (serine 473) and total AKT by Western blotting. BCL-XL was probed as a marker for CD40 stimulation. β-actin was used as a loading control for densitometric analysis. One representative blot from 3 CLL samples examined is shown. (B) shows a pooled data analysis of the effect of CD40 stimulation on levels of p-AKT in co-cultured CLL cells. In this and subsequent figures, each bar represents the mean ± SD, unless otherwise stated. (C) CLL cells were co-cultured for 24 and 48 h as in (A) but in the presence or absence of recombinant human IL-4 (10 ng/ml) or IL-21 (12.5 ng/ml). CLL cells were then harvested and analysed for levels of p-AKT (serine 473) and PTEN by Western blotting. One representative blot from 4 CLL samples examined is shown. (D) shows a pooled data analysis of the effect of CD40 stimulation on levels of p-AKT in co-cultured CLL cells as in (C). (E) shows a pooled data analysis of the effect of CD40 stimulation on levels of PTEN in co-cultured CLL cells as in (C).