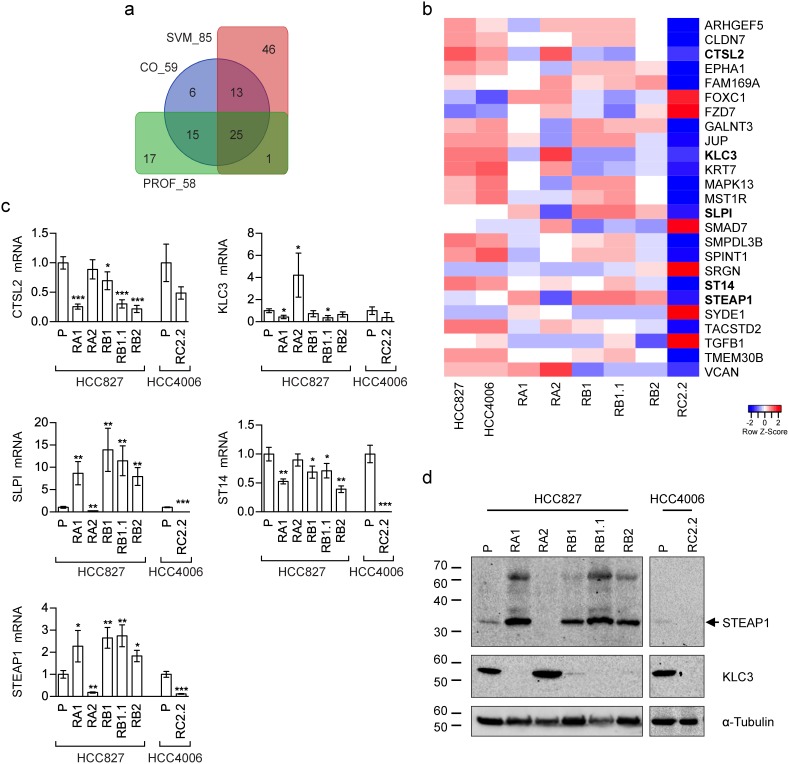
Figure 8. EMT-related gene subsets discriminating epithelial, mesenchymal and intermediate E/M phenotypes.
(a) Venn diagram showing overlaps among the three differently selected subsets of EMT-related genes. Abbreviations. CO_59: 59 EMT-related genes selected by cut-off on gene expression (CO); SVM_85: 85 EMT-related genes selected by support vector machines classification (SVM); PROF_58: 58 EMT-related genes selected by expression profile analysis (PROF). (b) Heatmap representing the relative expression levels across erlotinib-sensitive and erlotinib-resistant NSCLC cell lines for 25 genes shared by all the EMT-related gene subsets represented in (a). Data are row-scaled and rendered on a blue (lower expression) to red (higher expression) scale. Bold gene labels highlight the genes validated by qPCR. (c) qPCR analysis of CTSL2, KLC3, SLPI, ST14, and STEAP1 mRNAs normalised to rp-L31 mRNA and expressed relative to their levels in parental (P) cell lines (mean ± SD). qPCR data are representative of three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate significant t-test p-values in the comparison of a given derived cell line with the corresponding parental cell line: * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001. Only significant p-values are shown. (d) Western blot analysis of STEAP1 and KLC3 in the indicated parental (P) and erlotinib-resistant cell lines.