Figure 1. Generation and characterization of Spt5V1008D mutant ESCs.
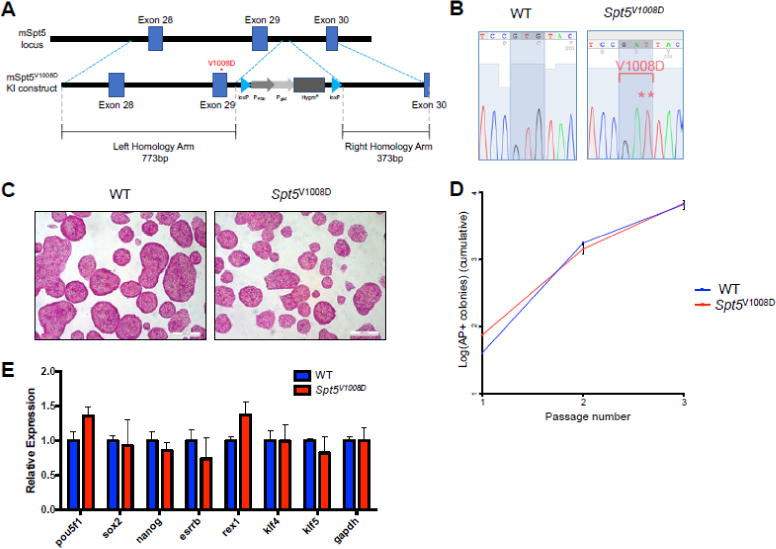
(A) Schematic of the murine Supt5h loci (exons 28 through 30) showing the wild-type and targeted allele that contains the V1008D mutation. The targeted allele contains a hygromycin resistance (HygroR) cassette flanked by LoxP sites.
(B) Sanger sequencing results of the wild-type and a homozygous clone. The mutated codon for V1008D is highlighted.
(C) Representative images of alkaline phosphatase staining of wild-type and Spt5V1008D homozygous ESCs.
(D) Clonal self-renewal assay for wild-type and Spt5V1008D ESCs (mean ± SEM, n=3)
(E) Quantitative RT-PCR comparing mRNA levels of ESC markers in wild-type and Spt5V1008D ESCs. Gene expression is normalized to Gapdh and presented as fold change relative to wild-type levels (n=3, mean ± SEM).
