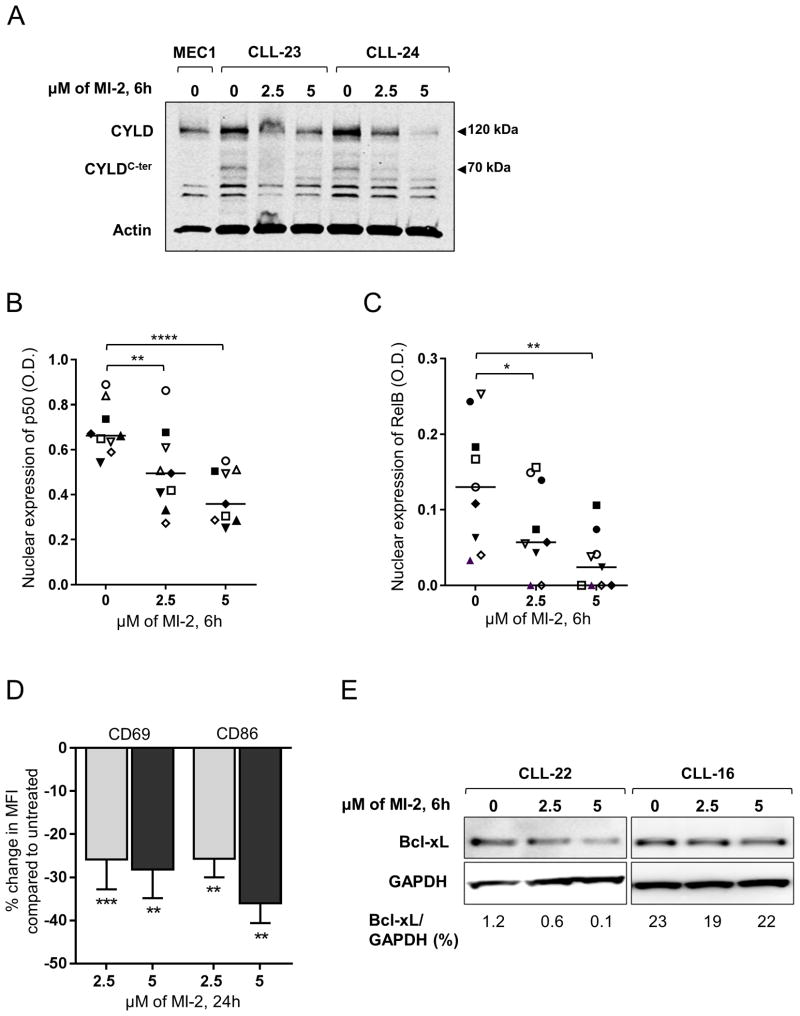
Figure 5. MI-2 inhibits CYLD cleavage, suppresses NF-κB translocation to the nucleus, and restores apoptosis in CLL.
(A) Immunoblot assay of whole cell lysates extracted from CD19-selected CLL cells collected from two patients showing the changes in total CYLD (120 kDa), and cleaved CYLD (CYLDC-ter, 70 kDa) following a 6h exposure to 2.5 and 5 μM of MI-2. Actin is shown as a loading control. (B, C) Nuclear expression of NF-κB subunits (B) p50 and (C) RelB determined by ELISA (N=9) following a 6h exposure to 2.5 and 5 μM of MI-2. Each patient is represented by a unique symbol; lines represent median values. (D) Primary CLL PBMC's (N=13) were incubated with or without 2.5 μM or 5 μM MI-2 for 24h. Shown is the % change in MFI in CD19+ CLL cells for activation markers CD69 and CD86 normalized to untreated control. (E) Immunoblot of two CLL patients showing change in Bcl-xL expression following a 6h exposure to 2.5 and 5 μM MI-2. All comparisons by paired Student t test.
*, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ****, P<0.0001.