Figure 1.
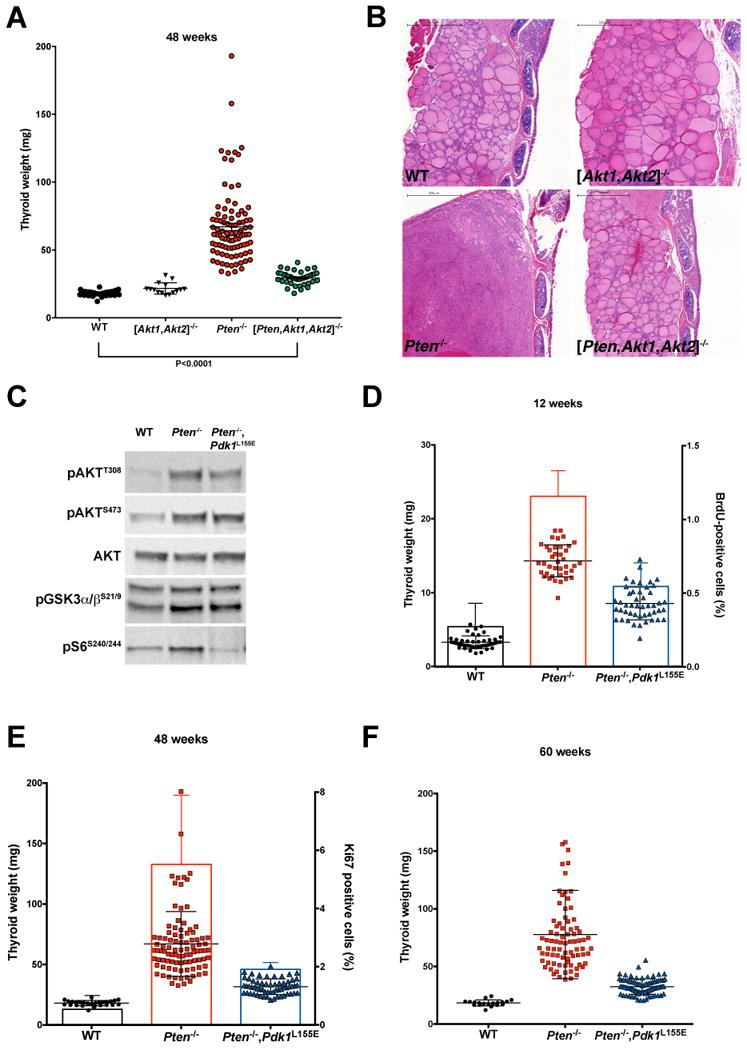
Genetic analysis of the role of AKT and PDK1-dependent AGC kinases in the development of thyroid hyperplasia. A, thyroid weight at 48 weeks of age for mice of the indicated genotypes. B, H&E staining of representative sections from thyroid glands dissected from 48-week old mice of the indicated genotypes. Bar: 500µm. C, Western blot analysis showing that the Pdk1 L155E allele does not affect AKT phosphorylation and activity, but completely impairs the activity of the PIF-pocket dependent AGC kinase S6K. D-F, thyroid weight at 12, 48, and 60 weeks of age, showing the effect of the Pdk1 L155E allele on the hyperplasia induced by Pten deletion. In addition, the thyroid proliferative index was measured by BrdU incorporation (D), or by Ki67 staining (E).
