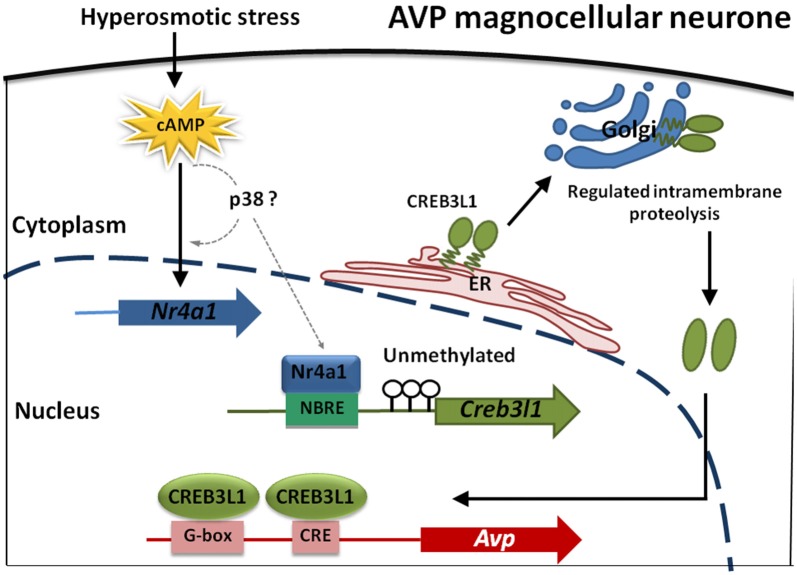
Figure 8.
Modeling transcriptional control of the Avp gene in magnocellular neurones of the hypothalamus. cAMP levels increase in magnocellular neurons in response to raised plasma osmolality resulting from DH. Our in vitro studies have indicated that p38 may increase Nr4a1 and also Creb3l1 mRNA expression but any direct actions in vitro and in magnocellular neurones remain to be established (dotted lines). What is known is that Nr4a1 expression increases in AVP magnocellular neurons alongside increased expression of Creb3l1 in the dehydrated rat. Due to an absence of methylation marks on the Creb3l1 promoter in vivo, Nr4a1 has the capacity to increase Creb3l1 transcription through it interactions with a single NBRE site in the promoter resulting in increased full-length Creb3l1 protein. Inactive Creb3l1 protein is anchored in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane. Upon stimulation by DH, Creb3l1 is transported to Golgi apparatus where it is activated by regulated intramembrane proteolysis (RIP). The N-terminal active form of Creb3l1 then enters the nucleus to activate transcription of Avp.