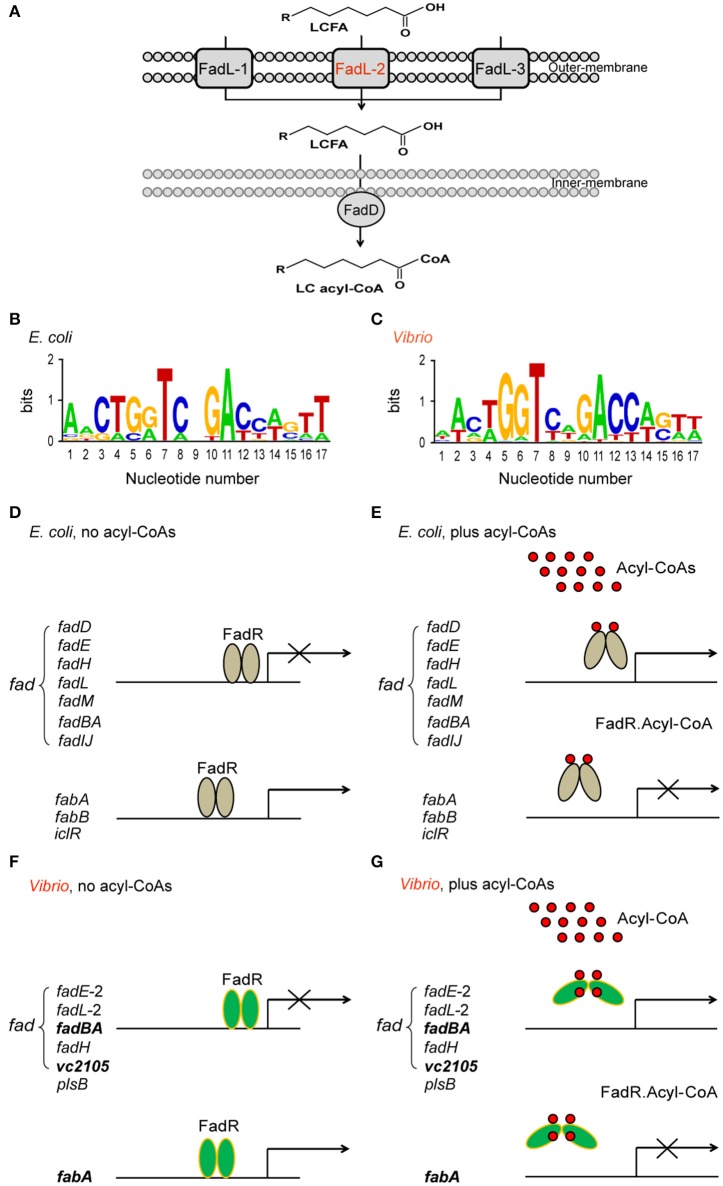
Figure 1.
Working model for Vibrio FadR-mediated fatty acid sensing and regulation. (A) Schematic representative for uptake and activation of long-chain fatty acids by FadL-FadD system of V. cholerae N16961. The long-chain fatty acids are transported by FadL membrane protein from the environment into periplasm and then activated by inner-membrane associated protein FadD to give LC acyl-CoA in cytosol. Among three putative FadR homologs encoded by V. cholerae N16961 genome, FadL2 (in red) is only one gene with a predicted FadR-binding site. LCFA is an abbreviation of long chain fatty acid. (B) Sequence logo for FadR-specific palindromes from E. coli MG1655. (C) Sequence logo for FadR-specific palindromes from Vibrio genus. The sequences of the known E. coli FadR sites were sampled from E. coli K-12 MG1655 (http://regprecise.lbl.gov/RegPrecise/regulon.jsp?regulon_id=10286), and the putative Vibrio FadR sites were collected from 9 Vibrio species (http://regprecise.lbl.gov/RegPrecise/sites.jsp?regulog_id=1762) (Novichkov et al., 2013). (D) E. coli FadR represses fad expression, but activates transcription of fabA/B and iclR on the condition without acyl-CoA thioesters. (E) Presence of long chain acyl-CoAs releases E. coli FadR protein from its cognate targets, resulting in an induction of fad expression and transcriptional inactivation of fabA/B and iclR. (F) Vibrio FadR represses the expression of limited fad members, whereas only activates fabA transcription on the condition with poor acyl-CoA species. (G) The generated long chain acyl-CoAs releases Vibrio FadR protein from its cognate targets, which consequently induces the expression of limited fad members, whereas only inactivates fabA transcription. The three representative genes (vc2105, fadBA, and fabA) are highlighted in bold and italic letters, whose ability of binding the Vibrio FadR regulator is demonstrated with EMSA (and/or SPR). The gray oval denotes E. coli FadR regulatory protein whereas the green oval denotes Vibrio FadR regulator. The small red circle represents the acyl-CoA pool. E. coli FadR has only one ligand-binding site in each monomer, whereas Vibrio FadR has two ligand-binding sites in each monomer.