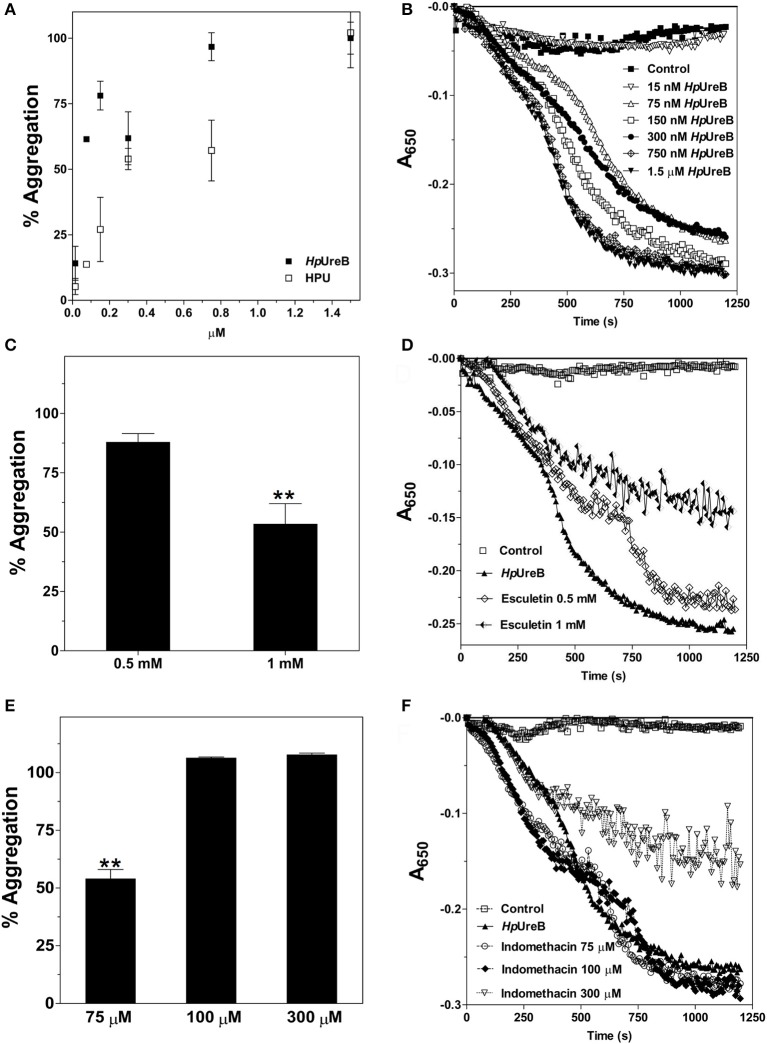
Figure 1.
Effects of HPU subunits on platelet aggregation. (A,B) HpUreB induces platelet aggregation in a dose dependent manner. (A) Aggregation of rabbit platelets was induced with the indicated final concentrations of HPU (open symbols, results taken from Wassermann et al., 2010) and HpUreB (closed symbols, this work). Aggregation induced by HPU or HpUreB at 1.2–1.4 μM was considered 100%. (B) Superimposed tracings of aggregation induced by different HpUreB concentrations as measured in the plate reader. (C–E) HpUreB-induced platelet aggregation depends on lipoxygenase-derived eicosanoid(s). Platelets were pretreated with the inhibitors of eicosanoids synthesis, esculetin (a 12-lipoxygenase inhibitor) (C,D) and indomethacin (a cyclooxygenase inhibitor) (E,F) at room temperature for 5 min without stirring. Aggregation was triggered by addition of 750 nM HpUreB (time zero), and after 2 min at 37°C stirring was turned on. Platelets response was monitored on SpectraMax M3 plate reader, with readings at 650 nm every 7 s for 20 min. Superimposed individual tracings of typical experiments are shown in (B,D,F). Aggregation responses were quantified as area under the tracings using SotfMax Pro 5.4.1 (A,C,E). Data are expressed as means ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined by ANOVA followed by Tukey-Kramer test. Values of **p < 0.01.