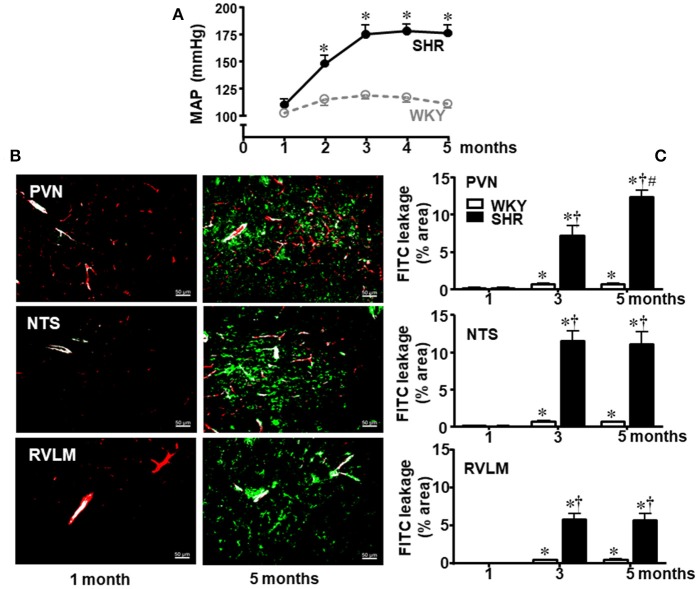
Figure 1.
Temporal changes of blood-brain barrier permeability within autonomic areas during 5 months' life span in sedentary spontaneously hypertensive (SHR) and normotensive rats (WKY). (A) Resting mean arterial pressure (MAP) values in SHR and WKY during 5 months' life span. n = 8 rats/subgroup. Significances (*P < 0.05) vs. WKY. (B) Images show the capillary profile (red, Rhodamine) and FITC extravasation (green) into the brain parenchyma in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN), nucleus of the tract solitary (NTS), and rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) in SHR aged 1 and 5 months. (C) Graphs compare FTIC leakage changes within the three autonomic areas of SHR and WKY groups from the 1st up to the 5th month. Values are the means of 8–12 slices, 4 rats in each subgroup. Significances (P < 0.05) *vs. 1st month; †vs. age-matched WKY; #vs. SHR aged 3 months.