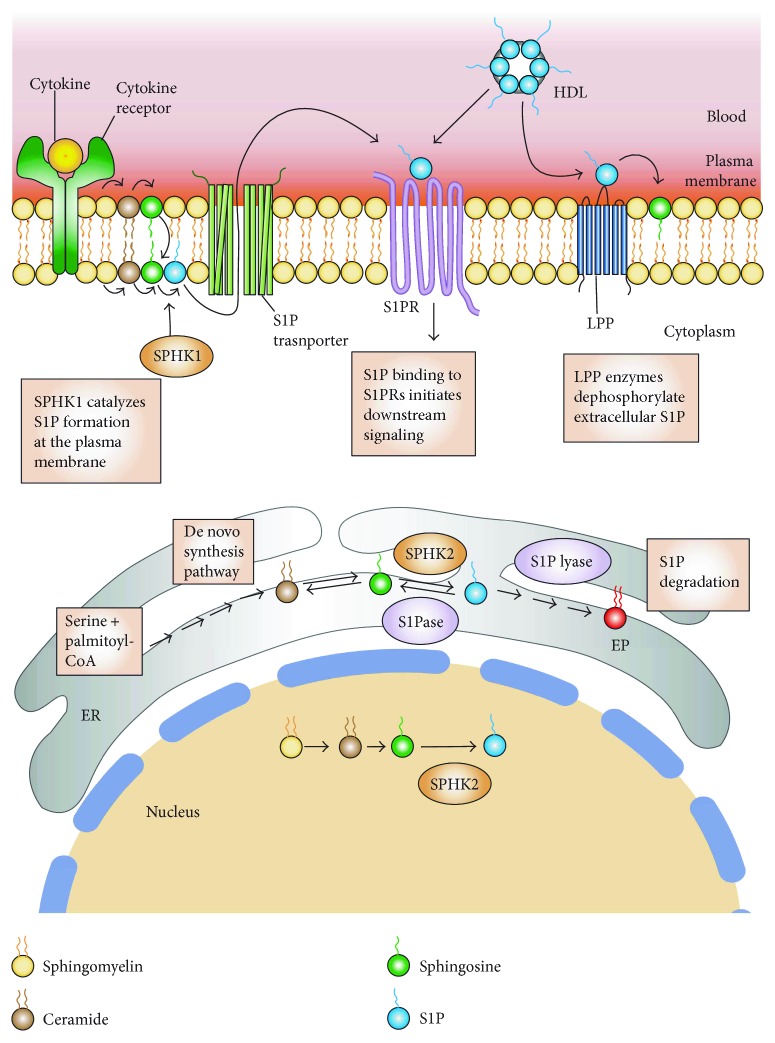
Figure 2.
S1P metabolism, synthesis, and inside-out signaling. Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is irreversibly degraded by S1P lyase into ethanolamine phosphate (EP) and trans-2-hexadecenal (Hex) and dephosphorylated to sphingosine by S1P phosphatase (S1Pase) in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and by nonspecific lipid phosphate phosphatases (LPP) in the plasma membrane. Extracellular sphingosine formed from S1P by LPPs can be taken up by cells and be converted back to S1P or other sphingolipids. In the blood, S1P is produced primarily by erythrocytes and transported bound to albumin and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). Extracellular S1P can activate S1P receptors (S1PRs). S1P is synthesized by sphingosine kinase 1 (SPHK1) in the plasma membrane by phosphorylating sphingosine and by SPHK2 at the ER and nucleus. S1P is produced in the plasma membrane in response to stimuli and is released by specific transporters to the extracellular space where it can bind to S1PRs and initiate downstream signaling pathways (inside-out signaling).