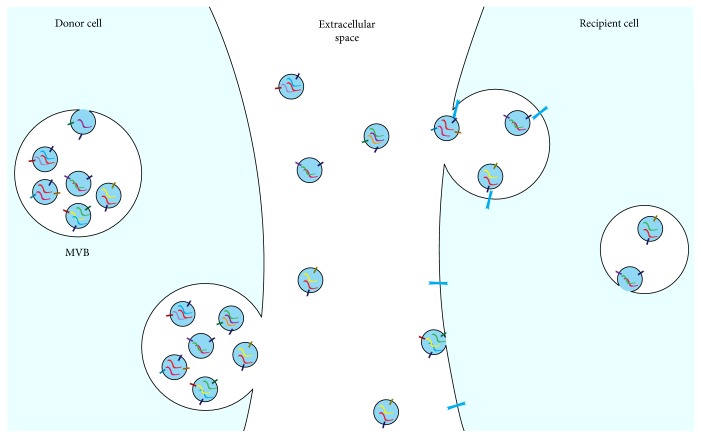
Figure 1.
Exosomes are formed by invaginations of intercellular vesicles such as endosomes, which then form multivesicular bodies (MVBs). Exosomes are released into the extracellular space by fusion of the MVB with the cell membrane. Recipient cells take up the exosomes through direct fusion with the cell membrane, through internalisation or through receptor-ligand interaction on the recipient cell membrane.