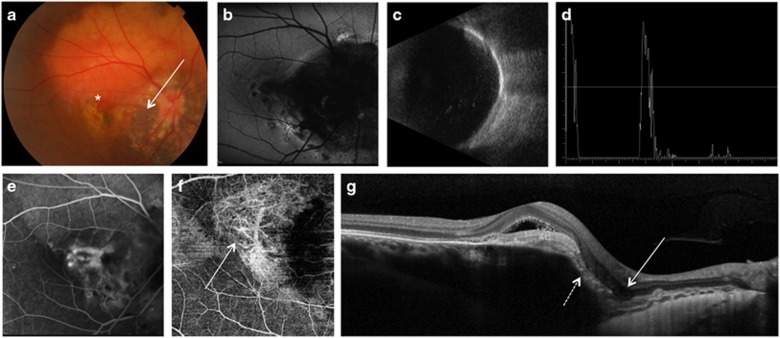
Figure 2.
Multimodal imaging of right eye in case 2. Fundus photograph (a) showed a large choroidal osteoma involving the macula, with a foveal retinal hemorrhage (asterisk); a pale area within the osteoma with visibility of underlying choroidal vessels around the optic disc was suggestive of decalcification of the tumor in the peripapillary area (arrow). Blue fundus autofluorescence (FAF) (b) showed a diffuse peripapillary hypoFAF area in correspondence of the decalcified portion of the choroidal osteoma. B scan echogram (c) showed a solid mass with acoustic shadowing. A scan ultrasonography (d) showed a high reflectivity of the lesion with sound attenuation posterior to the lesion. Axial length on A scan was 24.14 mm. Fluorescein angiography (e) showed an active leaking subfoveal CNV (arrow) which was visible on optical coherence tomography angiography (f, arrow). On optical coherence tomography scan (g) a well defined subretinal hyperreflective material was present in correspondence of the CNV; a focal choroidal excavation (arrow) was found adjacent to the CNV and in correspondence of the tumor decalcification which showed thinning of the overlying retinal pigment epithelium (dashed arrow). A full color version of this figure is available at the Eye journal online.