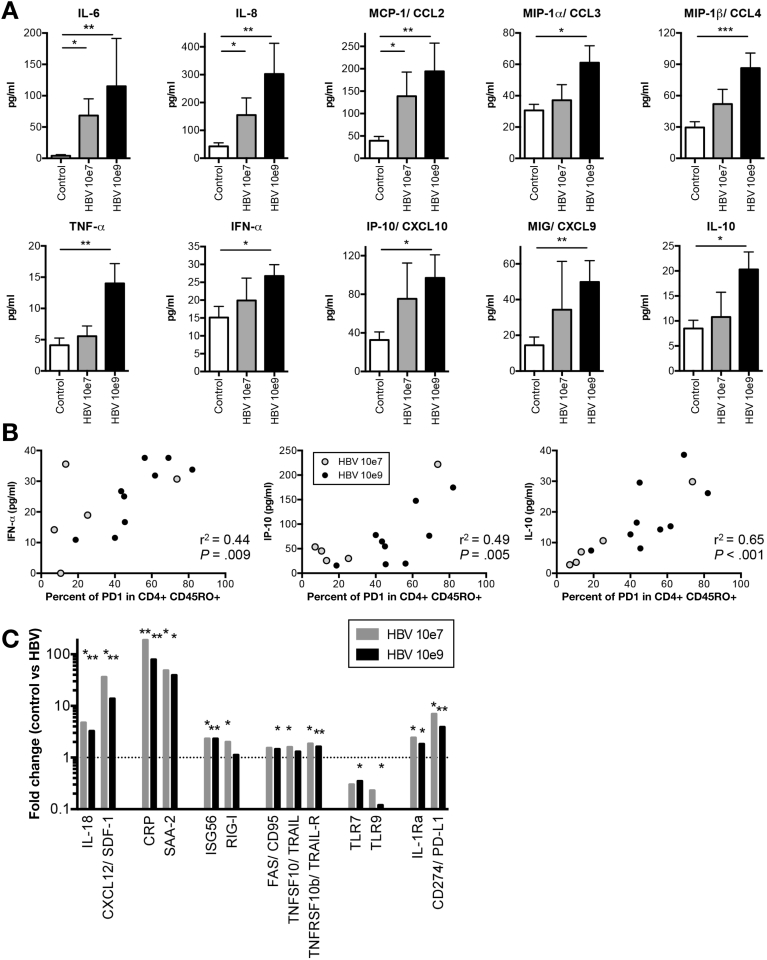
Figure 6.
Biomarker analysis in HBV-infected HIS-HUHEP mice. (A) Plasma from HIS-HUHEP control (n=11) and HBV-infected mice (inoculum 10e7, n=5; or 10e9, n=10) at endpoint were analyzed using human cytokine multiplex assay. No cross-reactivity with mouse cytokines was detected. Plasma levels of IL-1β, IL-1Ra, IL-2, IL-2R, IL-4, IL-12, IL-13, IL-15, IFN-γ, GM-CSF, and RANTES were similar between control and HBV-infected mice; while IL-5, IL-17, and Eotaxin were not detected (data not shown). (B) Correlation of PD-1+ memory CD4+ CD45RO+ T cells with either IFN-γ, or IP-10/CXCL10, or IL-10 plasma cytokines quantified in (A). Each dot represents a mouse: grey or black inoculated with, respectively, HBV 10e7 or HBV 10e9. (C) RT-qPCR analysis of liver samples from HIS-HUHEP control (n=14) and HBV-infected mice (inoculum 10e7, n=5; or 10e9, n=9). Fold changes in gene expression of HBV-infected compared with control mice are shown. Data was normalized to the internal control human GAPDH (hGAPDH) to account for differences in humanization levels on triplicate samples. Dotted line indicates fold change of 1. Histograms show the mean and SEM. Data from 14–20 wpi. Statistical significance: Mann Whitney U tests.