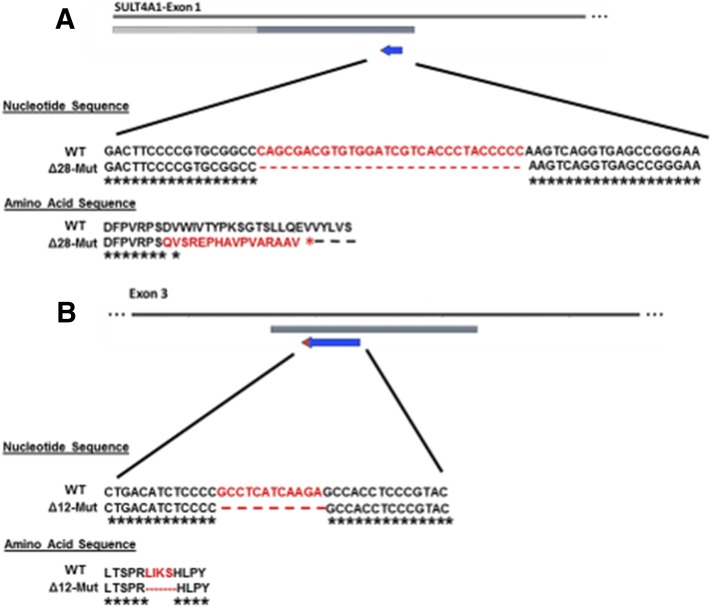
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of SULT4A1 mutations generated by CRISPR-Cas9. (A) Diagram of the Δ28 mutant SULT4A1 mouse line. CRISPR-Cas9 technology induced a 28-bp deletion within exon 1 that resulted in a frameshift mutation and premature stop codon at AA 62. (B) Diagram of the Δ12 mutant SULT4A1 mouse line. Gene editing induced a 12-bp in-frame deletion of the 4 AA immediately preceding the active site His. For both lines, SULT4A1 female founders were used to establish breeding colonies.