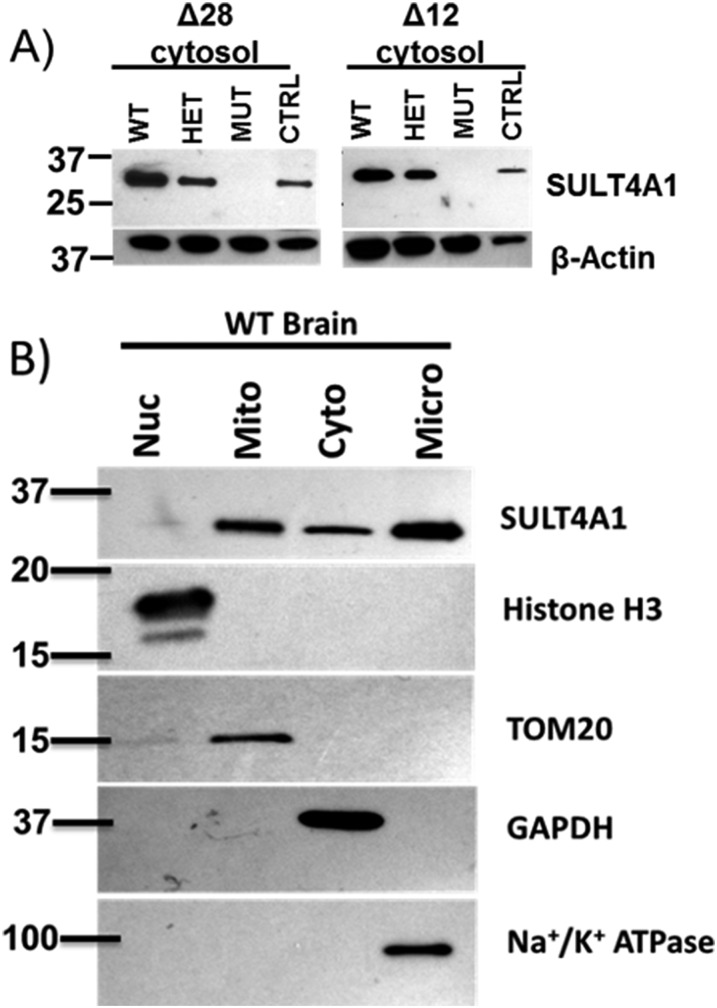
Fig. 2.
Characterization of SULT4A1 protein expression in Δ28 and Δ12 mutant mouse brains and subcellular localization of WT SULT4A1. WT, heterozygous, and homozygous Δ28 and Δ12 25-day-old mice were euthanized and whole brains were harvested. (A) WT, heterozygous (HET), and homozygous (MUT) Δ28 and Δ12 mice were probed for SULT4A1 protein expression. Human brain cytosol was used as a positive control (CTRL) for SULT4A1. For both strains, WT and heterozygotes showed positive staining for SULT4A1; however, Δ28 and Δ12 homozygotes were negative for SULT4A1. (B) Subcellular fractionation was used to generate nuclear (Nuc), mitochondrial (Mito), cytosolic (Cyto) and microsomal (Micro) fractions from WT adult mouse brain homogenates. Aliquots of each fraction (50 μg) were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted for SULT4A1. To determine the purity of subcellular fractions, marker proteins specific to each fraction were probed. Histone H3 was used to probe nuclear fraction purity, mitochondrial import receptor subunit TOM20 homolog (TOM20) was used as a marker protein for the mitochondrial fraction, GAPDH was used as a marker for the cytosolic fraction, and Na+/K+ ATPase was used to determine the microsomal fraction purity. SULT4A1 protein was detected in the mitochondrial, cytosolic, and microsomal fractions, and marker proteins demonstrated pure subcellular fractions.