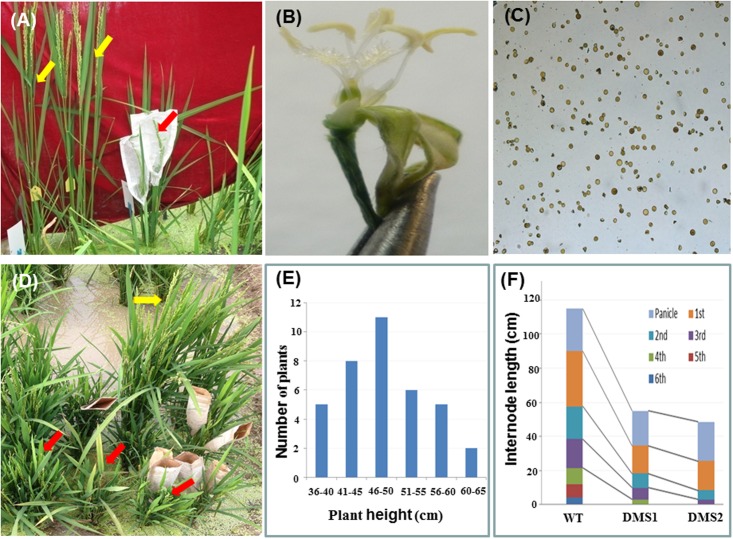
FIGURE 2.
Phenotypes of pTCK-RGGR-transgenic rice plants. Red arrows indicate the positive pTCK-RGGR-transgenic rice plants which are dwarf and male-sterile (DMS). Yellow arrows indicate the non-transgenic rice plants (wild-type, WT) which are male-fertile and with normal plant height. (A) Phenotype comparison between the DMS plant (red arrow) and the WT (NJ36, yellow arrows) grown in field. (B) A spikelet from the DMS plant in (A) showing the small and pale anthers. (C) I2-IK stained pollens from the DMS plant in (A), indicating that the poorly developed pollens are sterile. (D) Phenotype comparison between the DMS plants (red arrows) and the wild-type (Z0201, yellow arrow) grown in field. (E) Distribution of the 37 DMS plants generated in pTCK-RGGR-transformation of rice variety Z0201 in terms of plant height at ripening stage. (F) Comparison of length of plant height, panicle and internodes between the WT Z0201 and two DMS rice plants from (E), showing that the dwarfism of the DMS plants are mainly due to the reduction of the lower internodes.