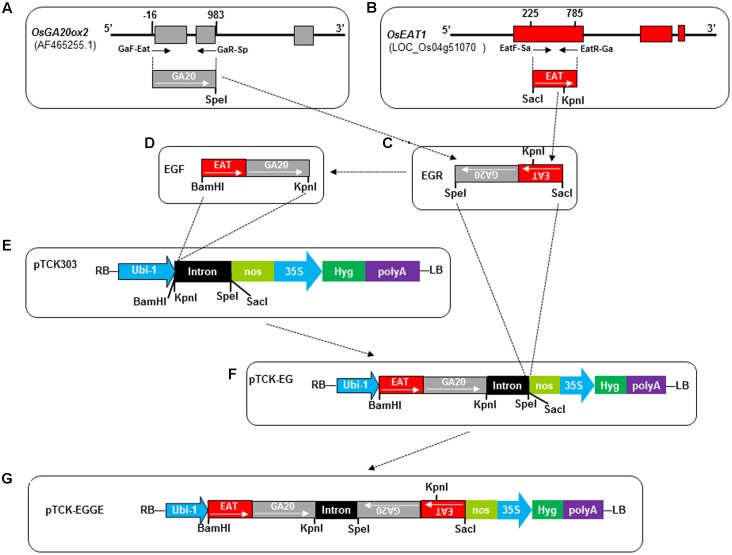
FIGURE 3.
Construction of hairpin RNAi vector pTCK-EGGE. Dash-dot lines/arrows indicate the relationship between the fragments or figure parts. (A) Schematic diagram of OsGA20ox2 gene structure and the fragment (GA20, 999 bp) for RNAi vector construction. The three exons are indicated by gray rectangles. The small arrows under the exons represent primers GaF-Eat and GaR-Sp whose 5′ positions related to the first nucleotide of the open reading frame are indicated by numbers above the exons. The restriction enzyme cutting site SpeI was introduced at the end of GA20 fragment. (B) Schematic diagram of OsEAT1 gene structure and the fragment (EAT, 561 bp) for RNAi vector construction. The three exons are indicated by red rectangles. Numbers above the 1st exon indicate the 5′ positions of the primers EatF-Sa and EatR-Ga presented by small arrows. The SacI site was introduced at the end of EAT by primer EatF-Sa. There is a native BamHI and KpnI restriction site at 42th and 365th nucleotide of the 561 bp-EAT fragment, respectively. (C) The joint antisense fragment EGR generated by overlap PCR with primers GaR-Sp and EatF-Sa. (D) The joint sense fragment EGF generated from the antisense fragment EGR by overlap PCR. The internal KpnI restriction site GGTACC in EGR was mutated as GGTCAG (Supplementary Table S4). (E) Intermediate vector pTCK303, with BamHI, KpnI, SpeI, and SacI restriction sites for exogenous fragment insertion. RB, right border; LB, left border; Ubi-1, the maize (Zea mays) ubiquitin promoter; nos, nos terminator; 35S, CAMV 35S promoter; Hyg, hygromycin phosphotransferase gene. The intron was a 478-bp rice intron amplified from rice (Wang et al., 2004). (F) Intermediate vector pTCK-EG generated by cloning the sense fragment EGF into the backbone vector pTCK303 at the BamHI and KpnI restriction sites. (G) Structure of the hairpin RNAi vector pTCK-EGGE.