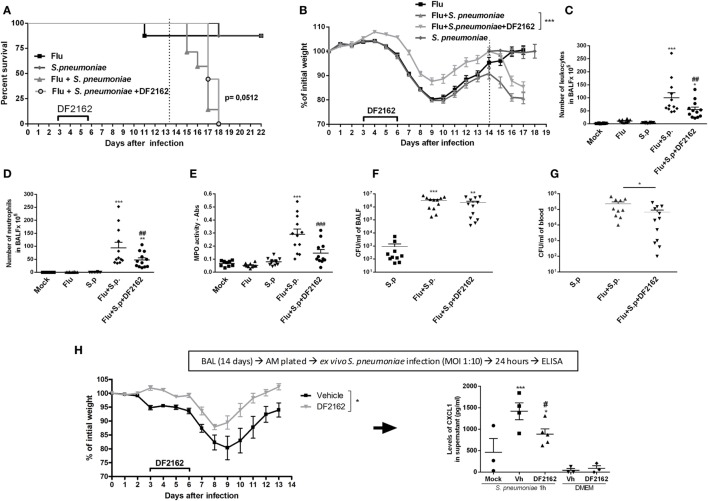
Figure 5.
Weight loss, neutrophils recruitment, and bacteria in blood and macrophage activation of secondary infected mice are reduced after CXCR1/2 treatment. Mice were infected with influenza A virus (IAV) (500 PFU, i.n.) and after 3, 4, 5, and 6 days of infection were treated twice a day with DF2162 (10 mg/kg—oral gavage) or the vehicle of the drug. After 14 days of IAV infection, mice were secondary infected with Streptococcus pneumoniae (103 CFU, i.n.). Single infections were also performed. Mock mice were instilled (i.n.) with PBS. The lethality [(A), n = 7–9 mice per group, representative of three independent experiment] and weight loss [(B), n = 20–35 mice per group, compilation of three independent experiments] were accompanied. In another experiment, mice under the same treatments and infection conditions were euthanized after 48 h after the second infection. Number of total leukocytes (C) and neutrophils (D) in the airways, neutrophils in the lungs [(E)— myeloperoxidase assay (MPO) assay] and bacteria in BALF (F) or in blood (G) were accessed (n = 4–6 mice per group, representative of two independent experiments). In another experiment, IAV-infected mice treated with vehicle or DF2162 as above were euthanized after 14 days; alveolar macrophages recovered from BALF were ex vivo infected with S. pneumoniae (MOI 1:10); after 24 h supernatant was collected for CXCL1 measurement (H). The results are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 when compared to Mock group; ##P < 0.01 and ###P < 0.001 when compared to Vehicle group.