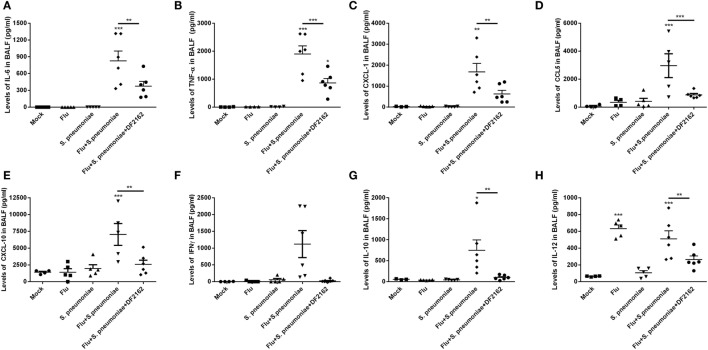
Figure 7.
CXCR1/2 antagonism during influenza A virus (IAV) primary infection reduced the levels of cytokines during pneumococcal secondary infection. Mice were infected with IAV (500 PFU, i.n.) and at 3, 4, 5, and 6 days after infection were treated twice a day with DF2162 (10 mg/kg—oral gavage) or the vehicle of the drug. The animals only received the drug during the IAV infection. After 14 days of IAV infection, mice were secondary infected with Streptococcus pneumoniae (103 CFU, i.n.). Single infections were also performed. Mock mice were instilled (i.n.) with PBS. After 48 h of the S. pneumoniae infection, mice were euthanized and the levels of IL-6 (A), TNF-α (B), CXCL1 (C), CCL5 (D), CXCL10 (E), IFN-γ (F), IL-10 (G), and IL-12 (H) were measured in the BAL fluid. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001, when compared with Vehicle mice or indicated groups (n = 5–6 mice per group, representative of two independent experiments).