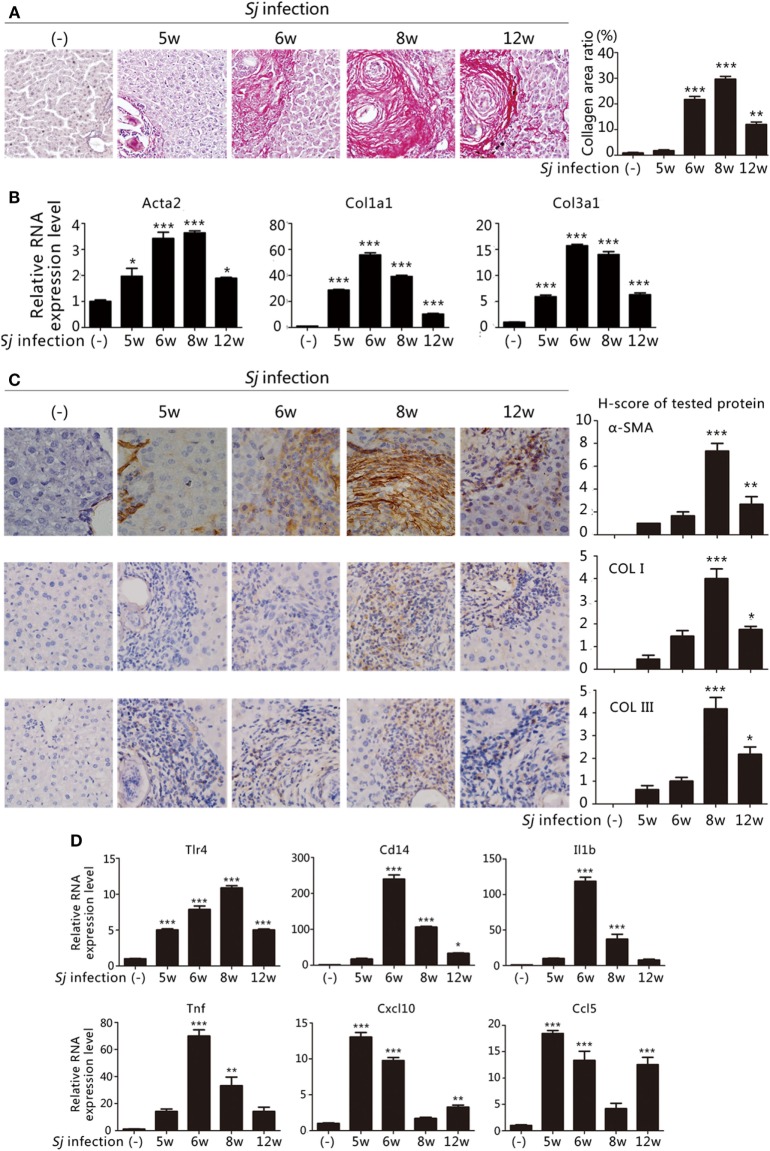
Figure 1.
Toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 pathway activation correlates with the extent of liver fibrosis post Schistosoma japonicum (Sj) infection. BALB/c mice were infected with 20 ± 3 infective cercariae of Sj for 5, 6, 8, and 12 weeks, and non-infected mice served as negative control. Liver tissues were fixed and stained with sirius red. A typical staining (200×) is shown in [(A) left]. Percentage of the total areas of morphometric collagen displayed with red color was calculated and shown in [(A) right]. (B) The steady-state mRNA expression levels of Acta2, Col1a1, and Col3a1 in the liver tissue of BALB/c mice were measured by quantitative-RT-PCR (qPCR). Gapdh was used as an internal reference; (C) The protein expression levels of α-SMA, COL I, and COL III in the mouse liver tissue were determined by immunohistochemical (IHC) assay (400×, left), and the semi-quantitative level of these proteins was analyzed using a modified H-score procedure (right); (D) The steady-state mRNA expression levels of TLR4 signal pathway-related molecules (Tlr4, Cd14, Il1b, Tnf, Cxcl10, and Ccl5) in the mouse liver tissue were measured by qPCR. Data are presented as mean ± SD from 7–10 mice per group. All experiments were performed twice. *P ≤ 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.