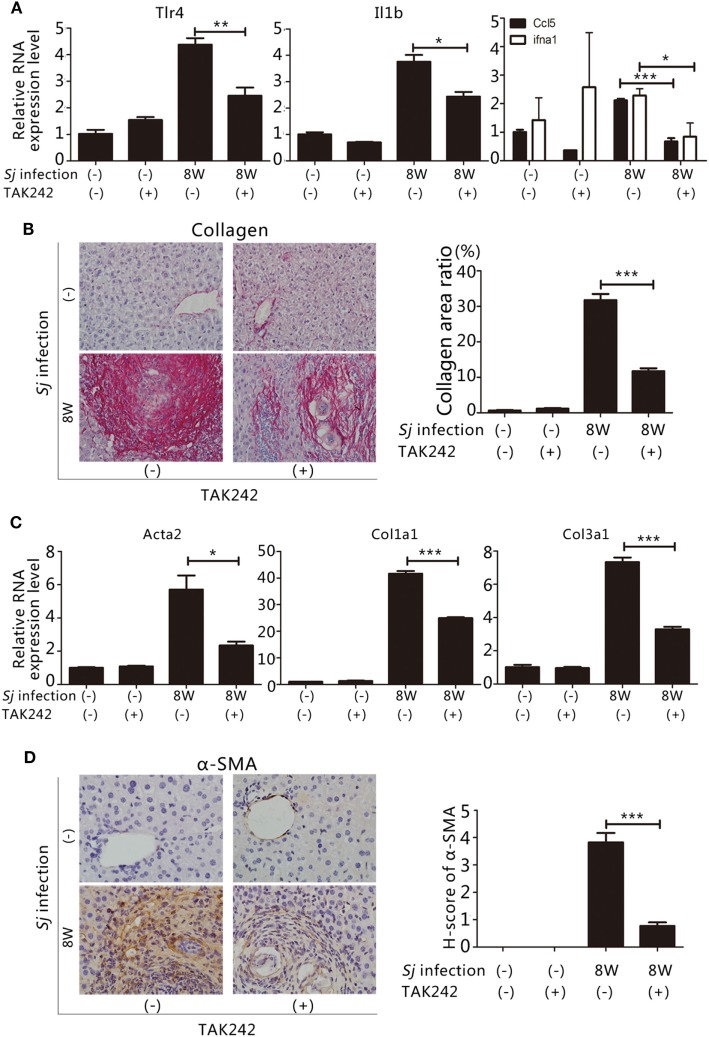
Figure 2.
Suppression of toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 signaling by TAK242 treatment decreases the severity of hepatic fibrosis post Schistosoma japonicum (Sj) infection. TLR4 signal pathway in BALB/c mice was blocked by intraperitoneal injection of TAK242 from week 4 to 8 post Sj infection. Non-infected mice with or without TAK242 treatment were used as controls. (A) The steady-state mRNA expression levels of Tlr4, Il1b, and ifna1, Ccl5 in the mouse liver were evaluated by qPCR to assess the inhibitory effect of TAK242 on TLR4 signaling. Gapdh was used as an internal control. Data are presented as mean ± SD from 7 to 10 mice per group; (B) A typical sirius red staining section (200×) of a mouse liver section is shown on the left panel. The semi-quantitative level of collagen deposition is shown on the right panel; (C) The steady-state mRNA expression levels of Acta2, Col1a1, and Col3a1 in the liver tissue were determined by qPCR; (D) A typical immunohistochemical (IHC) staining section (400×) for α-SMA, COL I, and COL III in the liver of BALB/c mice is shown on the left panel, and the modified H-score results are shown on the right panel. Data are presented as mean ± SD. All experiments were performed twice. *P ≤ 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.