Figure 8.
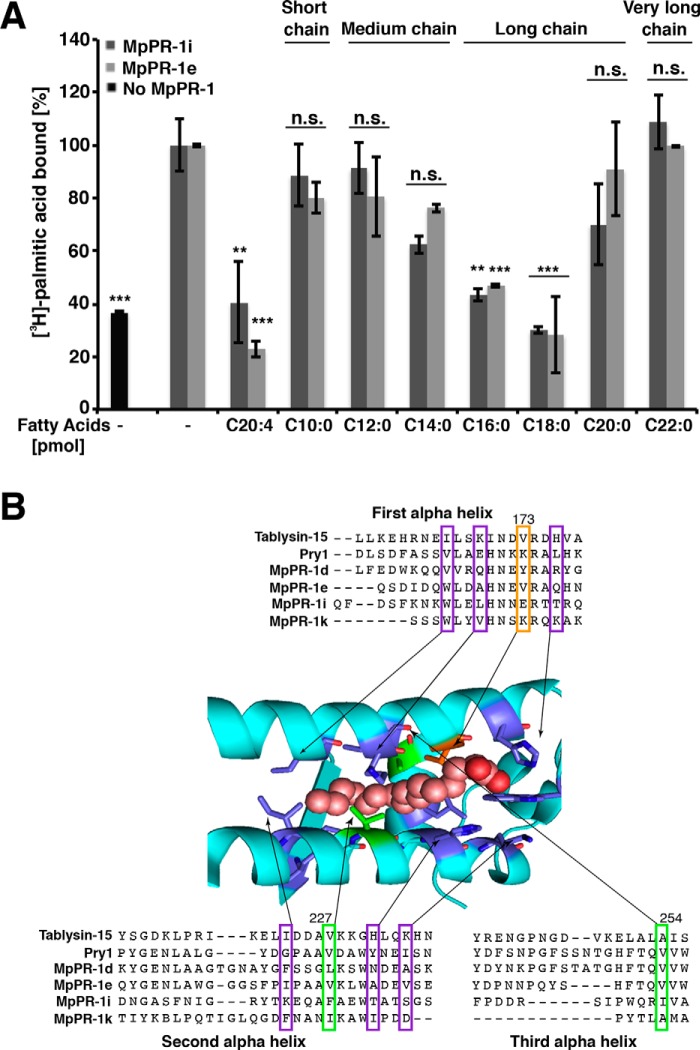
MpPR-1 family members bind saturated long chain and polyunsaturated fatty acids. A, fatty acid-binding specificity was assessed by a competition binding assay in which an equal concentration (50 pmol) of the unlabeled fatty acid of the indicated chain length and degree of unsaturation competes with the radiolabeled [3H]palmitic acid (50 pmol) for binding to the protein (100 pmol). The data represent the means ± S.D. of three independent experiments. Asterisks denote statistical significance relative to the control containing only the radiolabeled palmitic acid and purified MpPR-1i or MpPR-1e, respectively. ***, p < 0.0001; **, p < 0.001. n.s., not significant. B, sequence alignment around the fatty acid-binding pocket. The sequence of tablysin-15, yeast Pry1, and the M. perniciosa MpPR-1 family members analyzed in more detail are shown. The numbering on the top corresponds to the amino acid positions in Pry1. Valine at position 254 of Pry1 (boxed in green) is important for fatty acid binding (19). Key residues shown in colors are those forming the fatty acid binding pocket in tablysin-15 (17). B was adapted from Ref. 19.