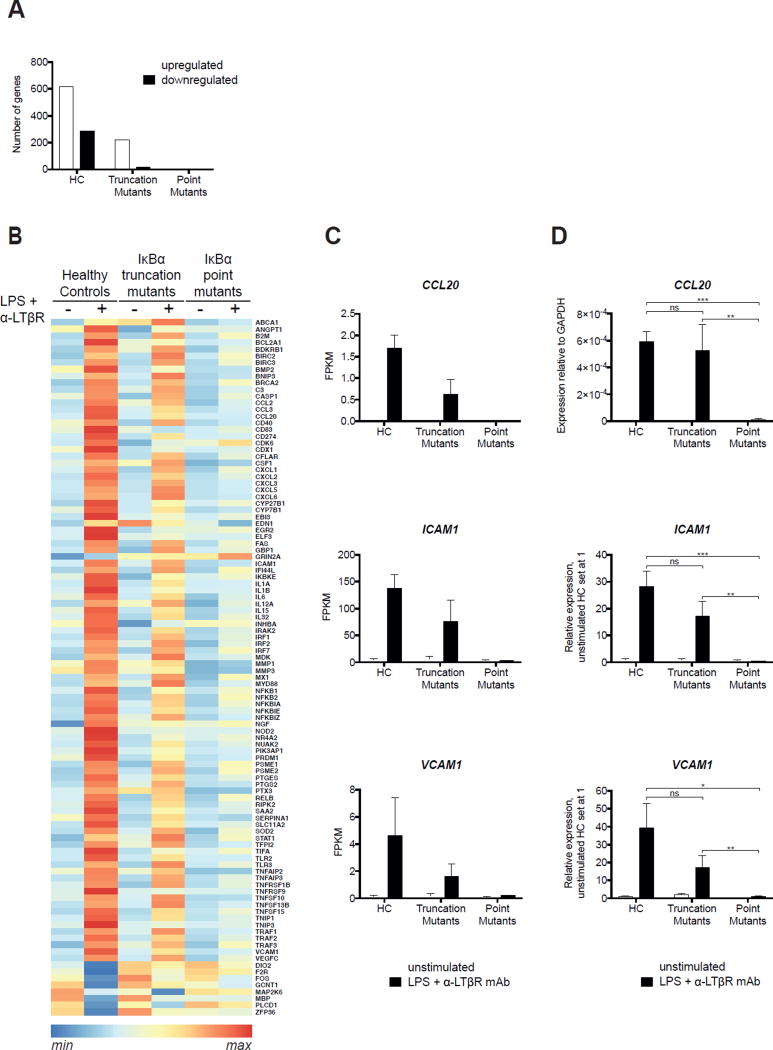
Figure 5. IκBα point mutants impair the induction of genes important for lymphorganogenesis more severely than IκBα truncation mutants.
A. Number of genes significantly (p<0.05) upregulated or downregulated by two folds or more in LPS+anti-LTβR mAb stimulated fibroblasts from healthy controls (n=3) and patients with IκBα truncation (n=2) and point mutations (n=2). B. Heat map analysis of NF-κB regulated genes the expression of which was significantly altered by LPS+anti-LTβR stimulation of normal fibroblasts. C. RNA-Seq analysis of the expression of CCL20, ICAM1 and VCAM1 mRNA in unstimulated and LPS+anti-LTβR mAb stimulated fibroblasts from healthy controls (n=3) and patients with IκBα truncation (n=2) and point mutations (n=2). Results are expressed as Fragments per Kilobase of Exon per Million (FPKM). Columns and bars represent the mean±SD for each of the three groups. D. q-PCR analysis of the expression of CCL20, ICAM1 and VCAM1 mRNA in unstimulated and LPS+anti-LTβR mAb stimulated fibroblasts from healthy controls (n=3) and patients with IκBα truncation (n=2) and point mutations (n=3). Results for ICAM1 and VCAM1 are expressed as the ratio of the gene of interest to GAPDH as calculated by the 2−ΔCt method relative to that of unstimulated healthy controls set at 1.0. Because CCL20 was undetectable in unstimulated fibroblasts, results are expressed as the ratio of CCL20 to GAPDH as calculated by the 2−ΔCt method. Columns and bars in D represent the mean±SD of three independent experiments. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; ns, not significant.