Figure 2.
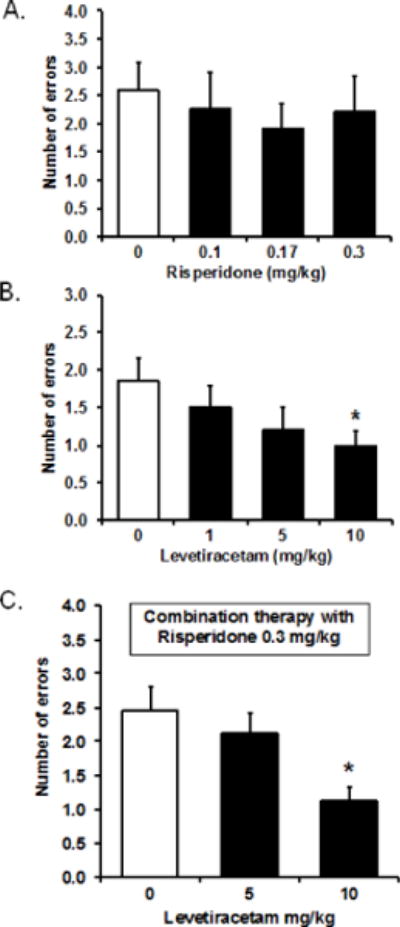
(A) Risperidone treatment at the doses tested had no effect on memory performance in the ketamine-exposed rats (n = 11) in the radial arm maze task. A repeated measures ANOVA showed no effect of treatment, F(3, 30) = 0.40, p = 0.758, or a dose response function, F(1, 10) = 0.55, p =0.477. (B) Levetiracetam treatment dose-dependently improved memory performance in ketamine-exposed rats (n = 14). A repeated measures ANOVA showed a marginally significant within-subject effect, F(3, 39) = 2.49, p = 0.075, with a significant within-subject contrast of the linear dose response function, F(1, 13) = 6.73, p = 0.022. The 10-mg/kg dose significantly reduced memory errors compared to vehicle treatment (0 mg/kg), t(13) = 2.26, p = 0.042 (paired sample t-test). (C) Levetiracetam treatment in the presence of risperidone preserved the efficacy of levetiracetam to dose-dependently lower the number of memory errors, F(2, 22) = 5.97, p = 0.008 for within-subject effect, and F(1, 11) = 13.28, p = 0.004 for linear dose response effect. Ketamine-exposed rats treated with levetiracetam at 10 mg/kg in combination with risperidone at 0.3 mg/kg (n = 12) had significantly fewer memory errors compared to when they were treated with risperidone at 0.3 mg/kg alone (levetiracetam 0 mg/kg), t(11) = 3.65, p = 0.004 (paired sample t-test).
