Figure 4.
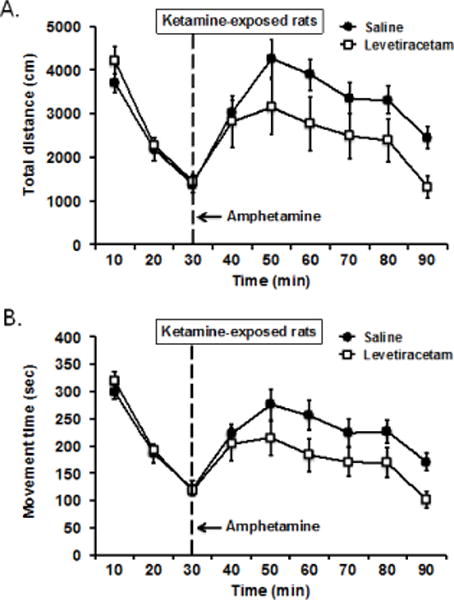
To assess the effect of levetiracetam on amphetamine-induced augmentation of locomotor activity, ketamine-exposed rats (n = 12) were given levetiracetam (10 mg/kg) or vehicle treatment on different test days prior to amphetamine challenge. (A) Compared to vehicle saline treatment, levetiracetam appeared to reduce the increased in distance travelled in response to amphetamine, but difference was not statistically significant, F(1, 11) = 2.99, p = 0.112 for treatment effect. (B) A second dependent measure using movement time showed that levetiracetam significantly lowered the amphetamine-induced increased in locomotor activity relative to vehicle saline, F(1, 11) = 5.01, p = 0.047 for treatment effect (see text for a more complete analysis).
