Figure 1. General scheme for TLR-dependent regulation of gene expression.
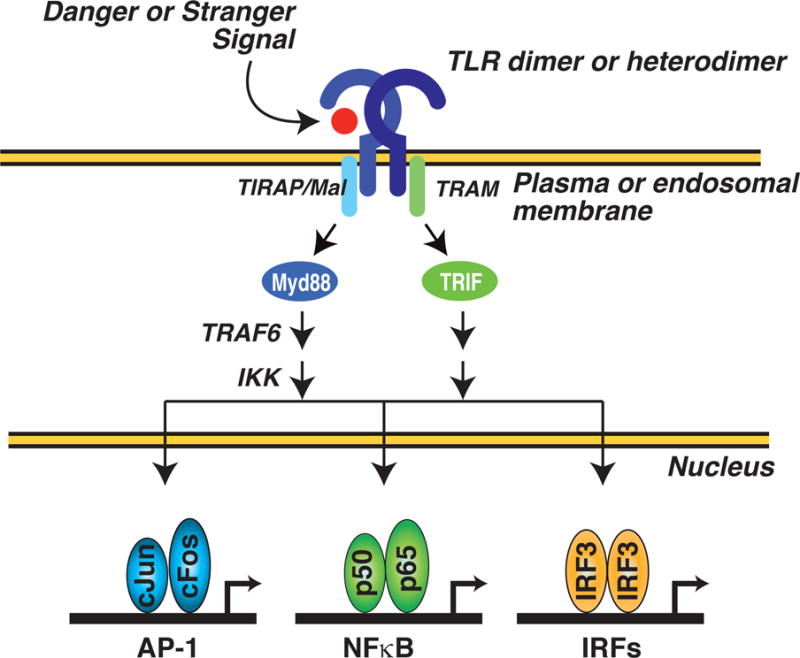
TLR dimers or heterodimers are activated by ‘danger’ (e.g., products of tissue injury) or ‘stranger’ (e.g., components of bacteria or viruses) signals. The liganded receptors couple to Myd88 and/or TRIF-dependent signal transduction pathways that function to activate latent transcription factors such as NFkB, AP-1 and interferon regulatory factors (IRFs). Upon activation, these factors bind to regulatory elements in target genes and positively regulate gene expression.
