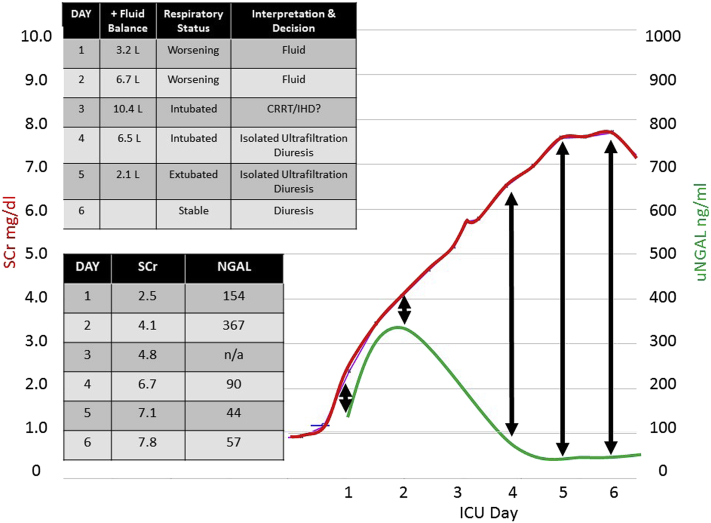
Figure 3.
Changes in urinary neutrophil gelatinase–associated lipocalin (uNGAL) assist with management (Case 5). The graph depicts changes in serum creatinine (SCr) (red) concurrent with changes in urine neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (uNGAL (green) over the first week of admission to the intensive care unit (ICU). This patient had a significant discordance between creatinine and NGAL, starting on day 2. Changes in NGAL influenced the management of this patient, obviating the need for a trip to the operating room, placement of a temporary hemodialysis catheter, and use of continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT). IHD, intermittent hemodialysis.