Figure 6.
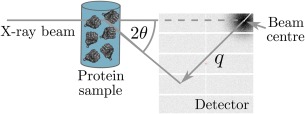
Diagram of a basic SAXS experiment. An X‐ray beam (typical energies range between 7 and 12.5 keV) is incident on a protein SAXS sample. Commonly the sample volume exposed to the beam is between 15 and 30 , with a protein concentration that usually ranges from 0.5 to 10 mg mL−1. The scattered radiation is collected on a detector. The symbol, in the figure, is termed the momentum transfer and is defined as where is half the scattering angle, and is the wavelength of the incident X‐ray beam. The detector images that are generated from the experiment can be processed and analysed to determine the overall shape and size of the protein molecule in the SAXS sample.
