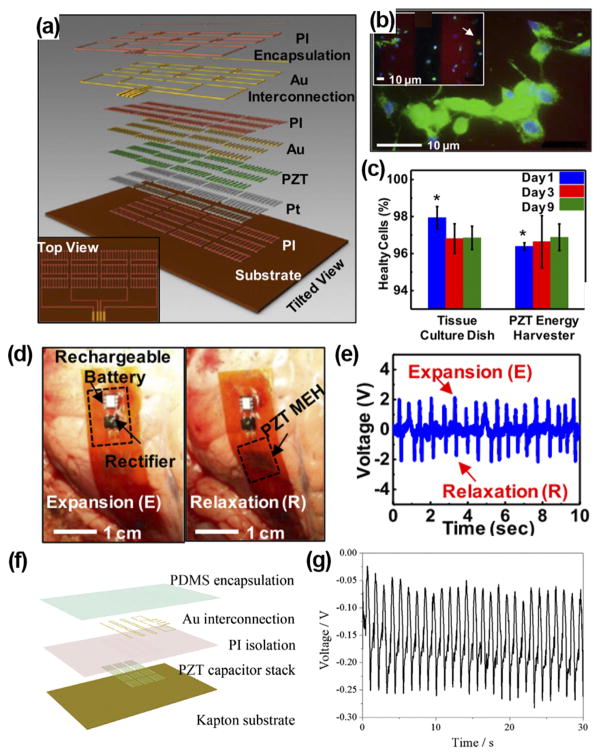
FIG. 2.
(a) Schematic illustration of a PZT nanofiber-based flexible NG. (b) Fluorescent image of a live/dead assay of rat smooth muscle cells on NG surface. Green, blue, and red colors represent live cells, intact nucleus, and dead cells, respectively. Inset shows dead cells pointed by the arrow. (c) Comparison between cells grown on device and cells grown on culture plates. ((d) and (e)) PZT NG attached to the heart of bovine (d) and corresponding output voltage (e). Reprinted with permission from Dagdeviren et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111(5), 1927 (2014). Copyright 2014 National Academy of Sciences. (f) Schematic structure of PZT thin film-based implantable NG. (g) Voltage outputs of the PZT i-PENG driven by heart beating when attached to the swine heart. Reprinted with permission from Lu et al., Sci. Rep. 5, 16065 (2015). Copyright 2015 Springer Nature.