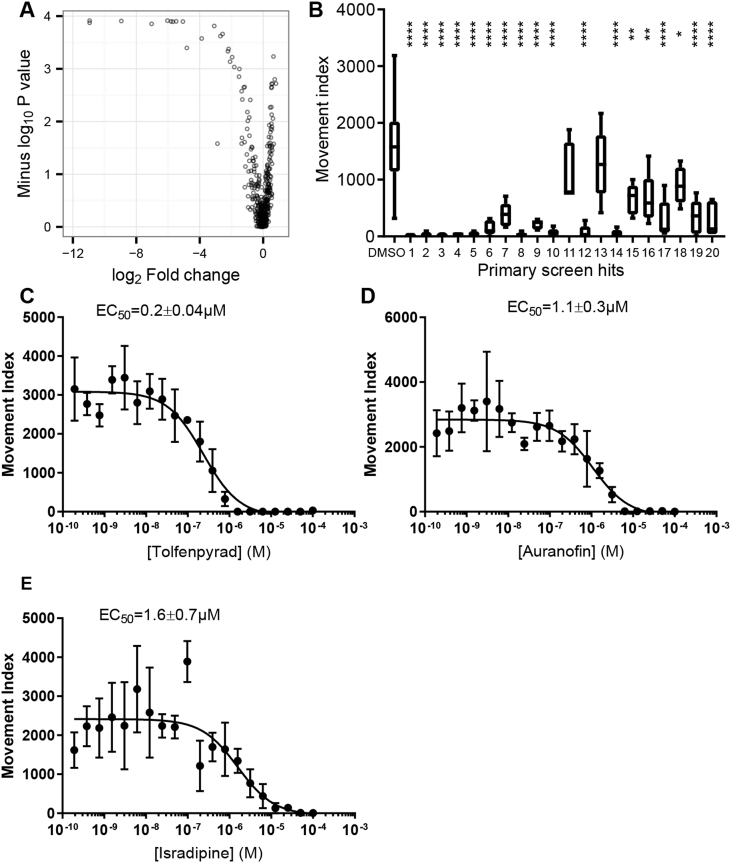
Fig. 7.
Screening the Pathogen Box in the C. elegans growth screen. (A) Volcano plot showing the results of the primary screen (n = 5 replicates per compound, concentration = 10 μM, each replicate was on different plates, over two experimental sessions). Each point represents one compound. Effective size is shown on the x axis, as log2-fold change (ratio of the median movement for the repeats of the compound to the median movement of DMSO-only wells). Statistical significance is shown on the y axis as the -log10 P value in the Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon test. A location at the top left of this plot indicates anthelmintic activity. (B) Secondary rescreen of hit compounds, using library material, in order of their activity in the primary screen. Statistical significance compared to DMSO-only control calculated by Dunnett's multiple comparison test (n = 5, * indicates P < 0.05, ** indicates P < 0.005, **** indicates P < 0.0005). (C,D,E) Concentration-response curves showing the activity of known anthelmintics – (C) tolfenpyrad, (D) auranofin, (E) isradipine – that were found in the Pathogen box screen retested using solid material (supplied by the Medicines for Malaria Venture) in the C. elegans growth assay. A concentration-response curve for mebendazole in the assay was presented in Fig. 3. Error bars indicate standard deviation, n = 4 wells per concentration per compound. Curve fitting was undertaken using three parameter log logistic model (Graphpad Prism).