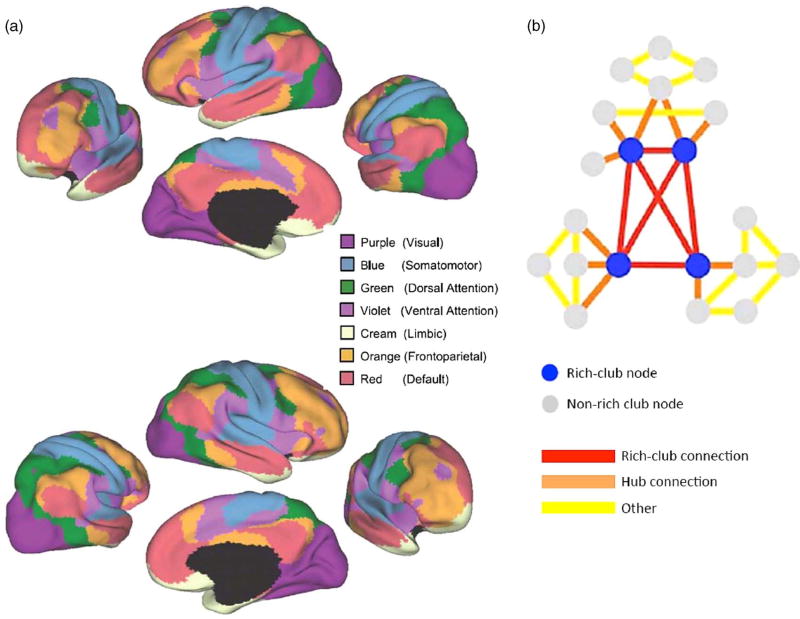
Fig. 4.
(a) Using rs-fcMRI mapping, a seven–network parcellation of the human cerebral cortex is presented, derived from 1,000 subjects from Yeo and colleagues (2011) (used with permission from the American Physiological Society). (b) Using both rs-fcMRI and DTI, van den Heuvel and Sporns (2011) derived a rich club network. When rich-club networks are inlaid within other networks, the complexity of network integration can be visualized. An injury to rich-club networks (blue circles and red connections) is much more disruptive to network integrity than damage to non-rich-club nodes and connections (gray circles, and orange and yellow connections) because of the dense interconnectedness of rich-club networks. In this analogy, the amount of damage is the same but the effects would be widely different because of the location and how networks would be affected. Adapted with permission from the Society for Neuroscience.