Figure 1. Overview of Systems Biology Study of HFD-Induced Insulin Resistance.
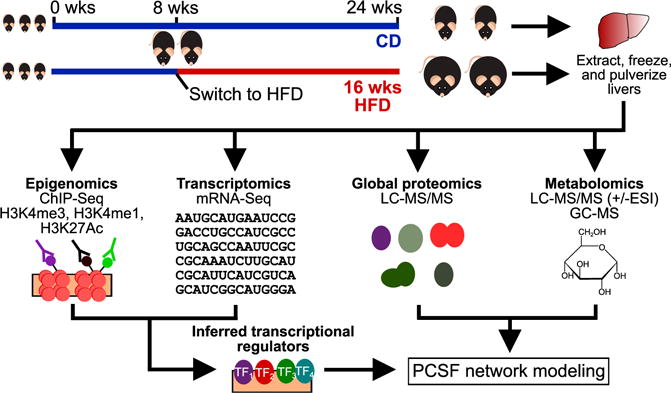
We fed 8-week-old male C57BL/6J mice a 16-week standard laboratory chow diet (CD) or a high-fat diet (HFD) to induce obesity and insulin resistance. At 24 weeks, we sacrificed the mice and extracted, flash froze, and pulverized their livers. We used these tissue samples to assay epigenomes, transcriptomes, proteomes, and metabolomes. We then used mRNA-seq (differential genes) and histone modification ChIP-seq (valleys within enriched peaks) data with known DNA-binding motifs to infer active transcriptional regulators. These regulators, along with differential proteins and metabolites, were used as input to the prize-collecting Steiner forest (PCSF) algorithm to uncover a network of interconnections among the data. ESI, electrospray ionization; GC-MS, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; LC-MS/MS, liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry; TF, transcription factor.
