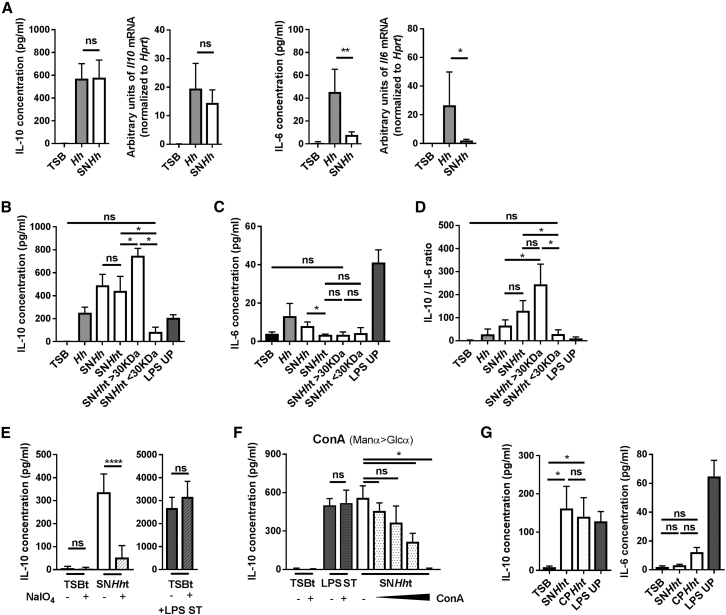
Figure 2.
H. hepaticus Produces a Large Soluble Polysaccharide-Inducing IL-10 Production in Macrophages
(A–G) M-CSF-differentiated BMDMs were stimulated for 3 hr with different culture fractions of H. hepaticus.
(A) mRNA and protein induction of the cytokines IL-10 and IL-6 after stimulation with control medium (TSB), H. hepaticus whole bacteria (Hh), or H. hepaticus-filtered cultured supernatant (SNHh).
(B–D) Induction of (B) IL-10, (C) IL-6, and (D) IL-10/IL-6 ratio after 3 hr stimulation with SNHh treated with enzymes and heat (SNHht), SNHht fractionated by size (SNHht > 30 kDa and SNHht < 30 kDa), and LPS UP.
(E) Induction of IL-10 after stimulation with TSBt or SNHht, treated with buffer (−) or sodium metaperiodate (+, NaIO4). Stimulation with TSBt ± NaIO4 and LPS ST is used as a positive control for IL-10 production by BMDMs.
(F) Induction of IL-10 after stimulation with TSBt, LPS ST, SNHht, or SNHht depleted using increasing concentrations of ConA-lectin beads (0.8%, 1.5%, 3%, and 6% v/v).
(G) Induction of IL-10 and IL-6 after stimulation with SNHht crude polysaccharide fraction extracted by a cold-ethanol precipitation method (CPHht).
Data from three independent experiments. Mann-Whitney test, p < 0.05. Mean ± SD. LPS UP, LPS ultrapure from E. coli O111:B4; LPS ST, LPS standard from E. coli O55:B5. See also Figure S2.