Figure 4. A summary of the role of O-GlcNAc in regulating essential brain functions.
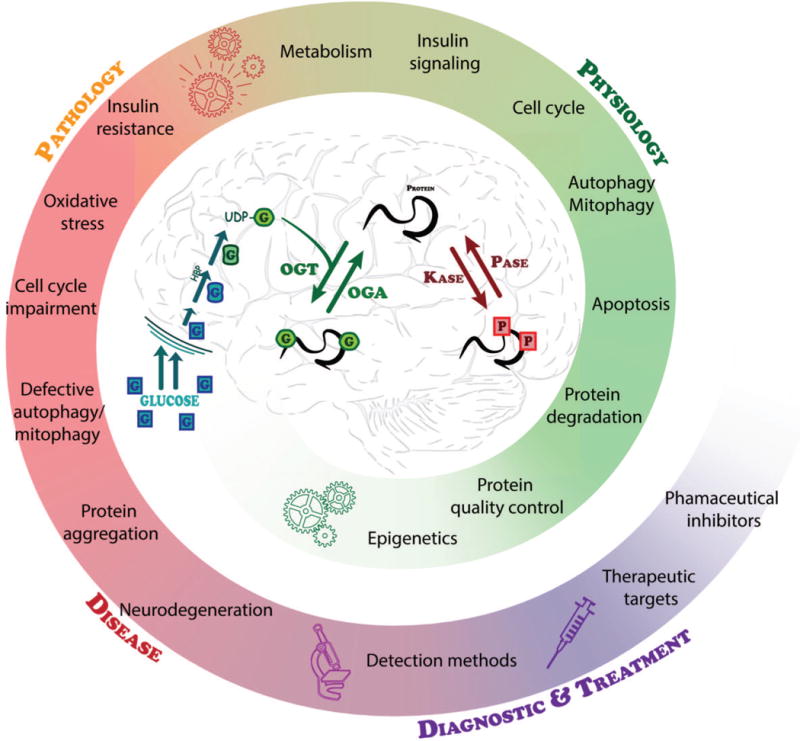
UDP-GlcNAc, the end product of the nutrient-sensitive HBP, is dynamically used by OGT to catalyze the addition of O-GlcNAc to substrate proteins. This cyclic modification is coordinately regulated with other PTMs such as phosphorylation to regulate the required intricacies of cellular processes. Deregulation of PTMs including O-GlcNAc leads to several pathologies that are associated with neurodegeneration. Methods for detecting O-GlcNAc and understanding its role in these pathologies continue to improve providing a strong foundation for considering targeted therapeutics based on individual or global protein O-GlcNAcylation and the activities of OGT and OGA.
