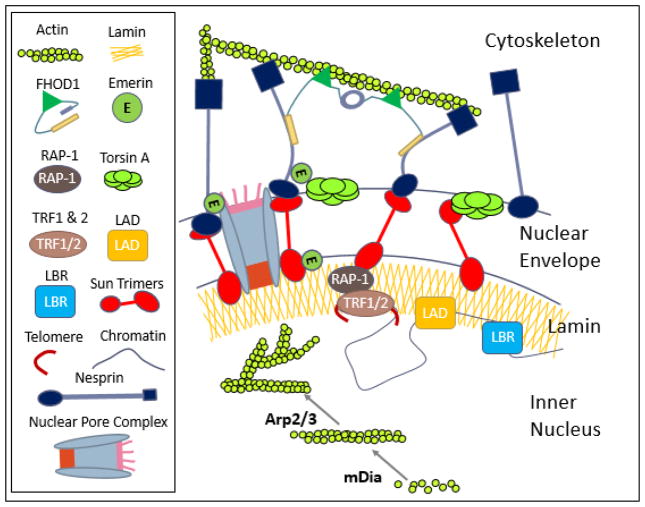
Figure 2. Hypothesis: Nucleoskeleton as a structural and regulatory organelle.
The schematic shows the nuclear envelope, nucleoskeleton and their binding partners that potentially play a role in MSC fate selection as well as facilitating the mechanical coupling between cytoplasmic and nuclear cytoskeletons. LINC complexes composed of Sun trimers and Giant Nesprin mechanically couple the actin cytoskeleton. For simplicity giant nesprin isoforms were indicated as nesprin and sun trimers were drawn as monomers. Mechanical coupling of actin and LINC involves a cytoplasmic formin FHOD1 that attaches nesprin and actin at multiple points for a more robust association. Torsin A may also facilitate the LINC assembly at the nuclear envelope. Inside the nucleus, G-actin is assembled into linear rods via mDia and into branched networks via the Arp2/3 complex, both of which can regulate availability of transcription factors and chromatin positioning. Sun1 directly binds to nuclear pore complexes as well as with RAP-1 to localize telomeres to the nuclear envelope. Chromatin interacts with nuclear structural elements to regulate gene expression including lamin B (through lamin B receptor, LBR), lamin A/C (via lamin associated domains, LADs), and actin filaments.