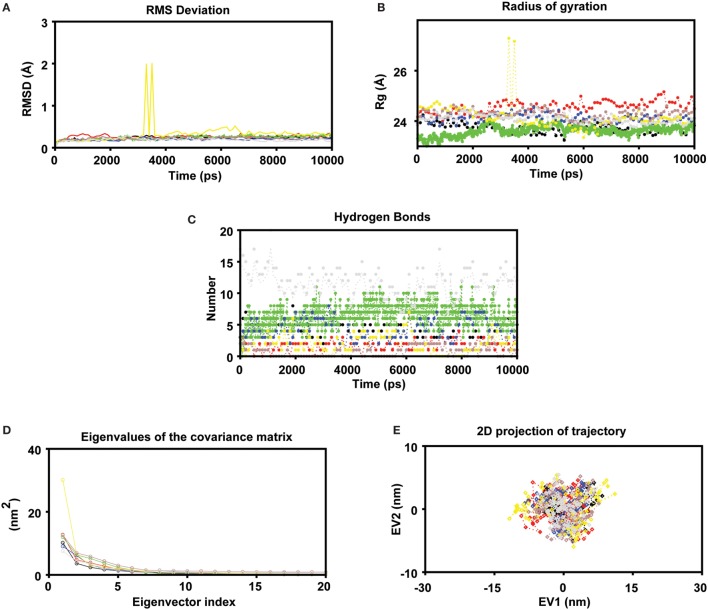
Figure 2.
MD simulations were carried out in GROMACS v5.0 (A) Molecular dynamics simulation study of human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-epitope complexes displaying the root mean square deviation (RMSD) of the backbone atoms during 10 ns simulations. *Black, Red, Green, Blue, Yellow, Brown (epitope complex), and Gray (control) color represents RMSD of each HLA-Epitope complexes. (B) Radius of gyration of the protein as a function of the simulation time averaged over 10 ns MD (C) Number of intermolecular hydrogen bonds (H-bonds) formed between the epitope and HLA for the entire duration of simulation. The criteria to measure H-bonds are based on cutoffs for the hydrogen-donor–acceptor angle (30°) and the donor–acceptor distance (0.35 nm) (where OH and NH groups were regarded as donors; and O and N were acceptors) (D) Principal component analysis. The eigenvalues plotted against the corresponding eigenvector indices obtained from the Cα covariance matrix constructed from 10 ns of the MD trajectory. First 20 eigenvectors were used for calculations (E) Projection of the motion of the HLA-Epitope complexes in phase space along the first two principal eigenvectors (EV1 and EV2). The cloud represents the projection of trajectories eigenvectors (EV1 and EV2).